Sequence and Series
NCERT Textbook Solution (Laptop/Desktop is best to view this page)
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 9
Sequences and Series Class 11
Chapter 9 Sequences and Series Exercise 9.1, 9.2, 9.3, 9.4, miscellaneous Solutions
Exercise 9.1 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 180
Q1 :
![]() Write the first five terms of the sequences
whose nth term is
Write the first five terms of the sequences
whose nth term is
Answer :
Substituting n = 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, we obtain
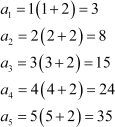 |
Therefore, the required terms are 3, 8, 15, 24, and 35.
Q2 :
![]() Write the first five terms of the sequences
whose nth term is
Write the first five terms of the sequences
whose nth term is
Answer :
Substituting n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, we obtain
Q3 :
Write the first five terms of the sequences whose nth term is an = 2n
Answer :
an = 2n
Substituting n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, we obtain
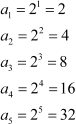 |
Therefore, the required terms are 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32.
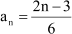 Q4 :
Q4 :
Write the first five terms of the sequences whose nth term is
Answer :
Substituting n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, we obtain
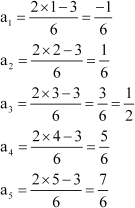 |
Q5 :
![]() Write the first five terms of the sequences
whose nth term is
Write the first five terms of the sequences
whose nth term is
Answer :
Substituting n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, we obtain
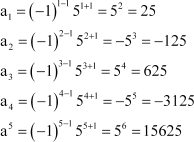 |
Therefore, the required terms are 25, β125, 625, β3125, and 15625.
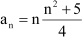 Q6 :
Q6 :
Write the first five terms of the sequences whose nth term is
Answer :
Substituting n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, we obtain
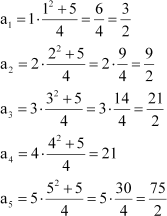 |
Q7 :
![]() Find the 17th term in the following
sequence whose nth term is
Find the 17th term in the following
sequence whose nth term is
Answer :
Substituting n = 17, we obtain
Substituting n = 24, we obtain
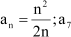 Q8 :
Q8 :
Find the 7th term in the following sequence whose nth term is
Answer :
Substituting n = 7, we obtain
![]()
Q9 :
![]() Find the 9th term in the following sequence whose nth term is
Find the 9th term in the following sequence whose nth term is
Answer :
Substituting n = 9, we obtain
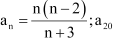 Q10 :
Q10 :
Find the 20th term in the following sequence whose nth term is
Answer :
Substituting n = 20, we obtain
![]()
Q11 :
Write the first five terms of the following sequence and obtain the corresponding series:
Answer :
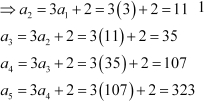 |
Hence, the first five terms of the sequence are 3, 11, 35, 107, and 323.
The corresponding series is 3 + 11 + 35 + 107 + 323 +
Q12 :
Write the first five terms of the following sequence and obtain the corresponding series:
Answer :
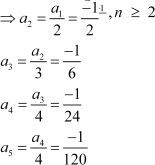 |
![]() Hence, the
first five terms of the sequence are
Hence, the
first five terms of the sequence are
Q13 :
Write the first five terms of the following sequence and obtain the corresponding series:
Answer :
 |
![]() Hence,
the first five terms of the sequence are 2, 2, 1, 0, and β1. The corresponding series is 2 + 2 + 1 + 0 + (β1) +
Hence,
the first five terms of the sequence are 2, 2, 1, 0, and β1. The corresponding series is 2 + 2 + 1 + 0 + (β1) +
Q14 :
The Fibonacci sequence is defined by
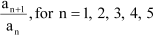 Find
Find
Answer :
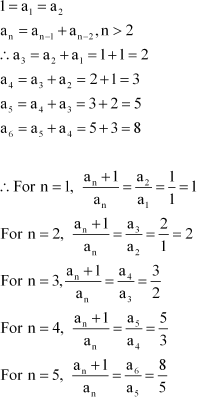
Exercise 9.2 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 185
Q1 :
Find the sum of odd integers from 1 to 2001.
Answer :
The odd integers from 1 to 2001 are 1, 3, 5, 1999, 2001. This sequence forms an A.P.
Here, first term, a = 1 Common difference, d = 2
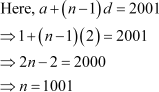
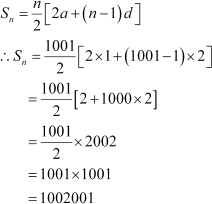
Thus, the sum of odd numbers from 1 to 2001 is 1002001.
Q2 :
Find the sum of all natural numbers lying between 100 and 1000, which are multiples of 5.
Answer :
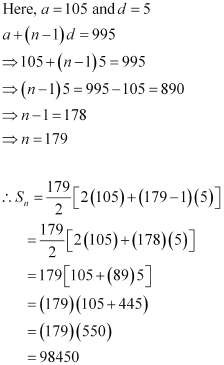 |
The natural numbers lying between 100 and 1000, which are multiples of 5, are 105, 110, 995.
Thus, the sum of all natural numbers lying between 100 and 1000, which are multiples of 5, is 98450.
![]()
Q3 :
In an A.P, the first term is 2 and the sum of the first five terms is one-fourth of the next five terms. Show that 20th term is -112.
Answer :
First term = 2
Let d be the common difference of the A.P. Therefore, the A.P. is 2, 2 + d, 2 + 2d, 2 + 3d, Sum of first five terms = 10 + 10d
Sum of next five terms = 10 + 35d According to the given condition,
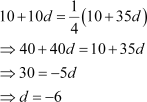
Thus, the 20th term of the A.P. is β112.
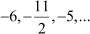 Q4 :
Q4 :
How many terms of the A.P. are needed to give the sum β25?
Answer :
![]() Let the sum of n terms of the given
A.P. be β25.
Let the sum of n terms of the given
A.P. be β25.
It is known that, , where n = number of terms, a = first term, and d = common difference Here, a = β6
![]()
Therefore, we obtain
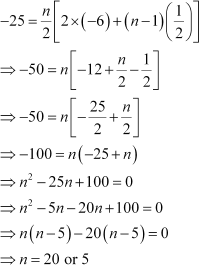
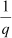
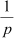 Q5 :
Q5 :
![]() In an A.P., if pth term is and qth term is , prove that the sum of first pq terms
In an A.P., if pth term is and qth term is , prove that the sum of first pq terms
is
Answer :
It is known that the general term of an A.P. is an = a + (n β 1)d
∴ According to the given information,
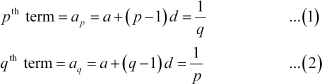 |
Subtracting (2) from (1), we obtain
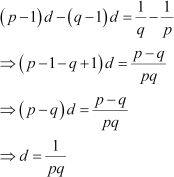 |
Putting the value of d in (1), we obtain
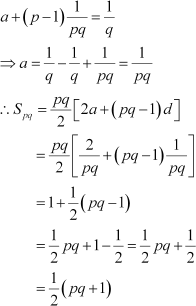 |
Q6 :
If the sum of a certain number of terms of the A.P. 25, 22, 19, is 116. Find the last term
Answer :
Let the sum of n terms of the given A.P. be 116.
Here, a = 25 and d = 22 β 25 = β 3
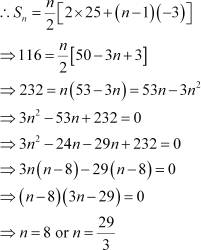
![]() However, n cannot be equal to .
Therefore, n = 8
However, n cannot be equal to .
Therefore, n = 8
∴ a8 = Last term = a + (n β 1)d = 25 + (8 β 1) (β 3)
= 25 + (7) (β 3) = 25 β 21
= 4
Thus, the last term of the A.P. is 4.
Q7 :
Find the sum to n terms of the A.P., whose kth term is 5k + 1.
Answer :
It is given that the kth term of the A.P. is 5k + 1.
kth term = ak = a + (k β 1)d
∴ a + (k β 1)d = 5k + 1
a + kd β d = 5k + 1
Comparing the coefficient of k, we obtain d = 5
a β d = 1
⇒ a β 5 = 1
⇒ a = 6
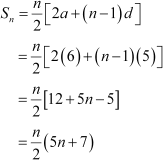
Q8 :
If the sum of n terms of an A.P. is (pn + qn2), where p and q are constants, find the common difference.
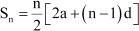 Answer :
Answer :
It is known that,
According to the given condition,
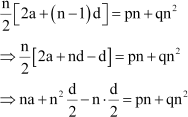 |
Comparing the coefficients of n2 on both sides, we obtain
∴ d = 2 q
Thus, the common difference of the A.P. is 2q.
Q9 :
The sums of n terms of two arithmetic progressions are in the ratio 5n + 4: 9n + 6. Find the ratio of their 18thterms.
Answer :
Let a1, a2, and d1, d2 be the first terms and the common difference of the first and second arithmetic progression respectively.
According to the given condition,
 |
Substituting n = 35 in (1), we obtain
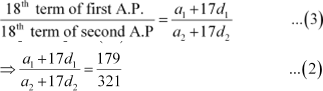 |
From (2) and (3), we obtain
Thus, the ratio of 18th term of both the A.P.s is 179: 321.
Q10 :
If the sum of first p terms of an A.P. is equal to the sum of the first q terms, then find the sum of the first (p+ q) terms.
Answer :
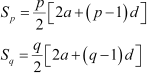 |
Let a and d be the first term and the common difference of the A.P. respectively. Here,
According to the given condition,
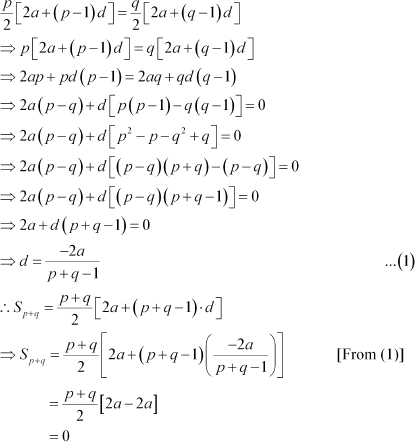
Thus, the sum of the first (p + q) terms of the A.P. is 0.
Q11 :
Sum of the first p, q and r terms of an A.P. are a, b and c, respectively. Prove that
Answer :
Let a1 and d be the first term and the common difference of the A.P. respectively. According to the given information,
Subtracting (2) from (1), we obtain
(p - 1)d - (q - 1)d = 2ap - 2bq⇒d(p - 1 - q + 1) = 2aq - 2bppq⇒d(p - q) = 2aq -
2bppq⇒d = 2(aq - bp)pq(p - q)............................. (4)
Subtracting (3) from (2), we obtain
Equating both the values of d obtained in (4) and (5), we obtain
aq - bppq(p - q) = br - qcqr(q - r)⇒aq - bpp(p - q) = br - qcr(q - r)⇒r(q - r)(aq - bp) = p(p - q)(br -
qc)⇒r(aq - bp)(q - r) = p(br - qc)(p - q)⇒(aqr - bpr)(q - r) = (bpr - cpq)(p - q)
Dividing both sides by pqr, we obtain
Thus, the given result is proved.
Q12 :
The ratio of the sums of m and n terms of an A.P. is m2: n2. Show that the ratio of mth and nth term is (2m - 1): (2n - 1).
Answer :
Let a and b be the first term and the common difference of the A.P. respectively. According to the given condition,
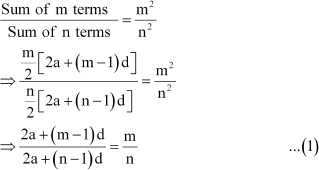
Putting m = 2m β 1 and n = 2n β 1 in (1), we obtain
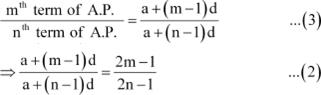 |
From (2) and (3), we obtain
Thus, the given result is proved.
Q13 :
If the sum of n terms of an A.P. is and its mth term is 164, find the value of m.
Answer :
Let a and b be the first term and the common difference of the A.P. respectively.
am = a + (m β 1)d = 164 (1) Sum of n terms,
Here,
n2 [2a + nd - d] = 3n2 + 5n⇒na + d2n2 - d2n = 3n2 + 5n⇒d2n2 + (a - d2)n = 3n2 + 5n
Comparing the coefficient of n2 on both sides, we obtain
Comparing the coefficient of n on both sides, we obtain
Therefore, from (1), we obtain 8 + (m β 1) 6 = 164
⇒ (m β 1) 6 = 164 β 8 = 156
⇒ m β 1 = 26
⇒ m = 27
Thus, the value of m is 27.
Q14 :
Insert five numbers between 8 and 26 such that the resulting sequence is an A.P.
Answer :
Let A1, A2, A3, A4, and A5 be five numbers between 8 and 26 such that 8, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, 26 is an A.P.
Here, a = 8, b = 26, n = 7 Therefore, 26 = 8 + (7 - 1) d
⇒ 6d = 26 - 8 = 18
⇒ d = 3
A1 = a + d = 8 + 3 = 11
A2 = a + 2d = 8 + 2 x 3 = 8 + 6 = 14
A3 = a + 3d = 8 + 3 x 3 = 8 + 9 = 17
A4 = a + 4d = 8 + 4 x 3 = 8 + 12 = 20
A5 = a + 5d = 8 + 5 x 3 = 8 + 15 = 23
Thus, the required five numbers between 8 and 26 are 11, 14, 17, 20, and 23.
 Q15 :
Q15 :
If is the A.M. between a and b, then find the value of n.
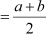 Answer :
Answer :
A.M. of a and b
According to the given condition,
 |
Q16 :
Between 1 and 31, m numbers have been inserted in such a way that the resulting sequence is an A.P. and the ratio of 7th and (m - 1)th numbers is 5:9. Find the value of m.
Answer :
Let A1, A2, Am be m numbers such that 1, A1, A2, Am, 31 is an A.P. Here, a = 1, b = 31, n = m + 2
∴ 31 = 1 + (m + 2 β 1) (d)
⇒ 30 = (m + 1) d
![]()
A1 = a + d
A2 = a + 2d
A3 = a + 3d
∴ A7 = a + 7d
Amβ1 = a + (m β 1) d
According to the given condition,
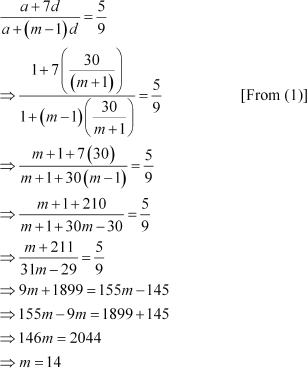 |
Thus, the value of m is 14.
![]()
Q17 :
A man starts repaying a loan as first installment of Rs. 100. If he increases the installment by Rs 5 every month, what amount he will pay in the 30th installment?
Answer :
The first installment of the loan is Rs 100.
The second installment of the loan is Rs 105 and so on. The amount that the man repays every month forms an A.P. The A.P. is 100, 105, 110,
First term, a = 100 Common difference, d = 5 A30 = a + (30 - 1)d
= 100 + (29) (5)
= 100 + 145
= 245
Thus, the amount to be paid in the 30th installment is Rs 245.
Q18 :
The difference between any two consecutive interior angles of a polygon is 5°. If the smallest angle is 120°, find the number of the sides of the polygon.
Answer :
The angles of the polygon will form an A.P. with common difference d as 5° and first term a as 120°. It is known that the sum of all angles of a polygon with n sides is 180° (n β 2).
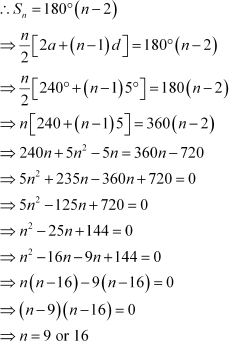
Exercise 9.3 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 192
Q1 :
![]() Find the 20th and nthterms of the G.P.
Find the 20th and nthterms of the G.P.
Answer :
The given G.P. is ![]() Here, a = First term =
Here, a = First term = ![]()
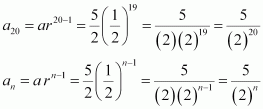 |
r = Common ratio =
![]()
Q2 :
Find the 12th term of a G.P. whose 8th term is 192 and the common ratio is 2.
Answer :
Common ratio, r = 2
Let a be the first term of the G.P.
∴ a8 = ar 8β1 = ar7
⇒ ar7 = 192
a(2)7 = 192
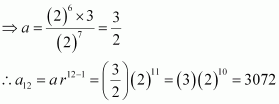 |
a(2)7 = (2)6 (3)
![]()
Q3 :
The 5th, 8th and 11th terms of a G.P. are p, q and s, respectively. Show that q2 = ps.
Answer :
Let a be the first term and r be the common ratio of the G.P. According to the given condition,
a5 = a r5β1 = a r4 = p (1) a8 = a r8β1 = a r7 = q (2) a11 = a r11β1 = a r10 = s (3)
 |
Dividing equation (2) by (1), we obtain
Dividing equation (3) by (2), we obtain

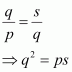 |
Equating the values of r3 obtained in (4) and (5), we obtain
Thus, the given result is proved.
![]()
Q4 :
The 4th term of a G.P. is square of its second term, and the first term is -3. Determine its 7th term.
Answer :
Let a be the first term and r be the common ratio of the G.P.
∴ a = -3
It is known that, an = arn-1
∴a4 = ar3 = (-3) r3 a2 = a r1 = (-3) r
According to the given condition,
(-3) r3 = [(-3) r]2
⇒ -3r3 = 9 r2
⇒ r = -3
a7 = a r 7-1 = a r6 = (-3) (-3)6 = - (3)7 = -2187
Thus, the seventh term of the G.P. is -2187.
Q5 :
Which term of the following sequences:
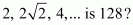
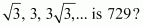 (a) (b) (c)
(a) (b) (c) 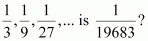 Answer :
Answer :
(a) The given sequence
is ![]() Here, a = 2 and r =
Here, a = 2 and r = ![]()
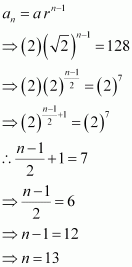 |
Let the nth term of the given sequence be 128.
Thus, the 13th term of the given sequence is 128.
(b) The given sequence is ![]() Here,
Here, ![]()
Let the nth term of the given sequence be 729.
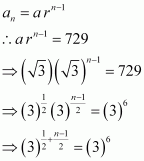
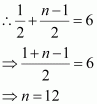
Thus, the 12th term of the given sequence is 729.
(c) The given sequence
is ![]() Here,
Here, ![]()
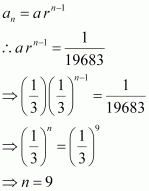 |
Let the nth term of the given sequence be
Thus, the 9th term of the given sequence is ![]() .
.
![]()
Q6 :
For what values of x, the
numbers ![]() are in G.P?
are in G.P?
Answer :
The given numbers are ![]() . Common ratio =
. Common ratio = 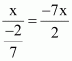
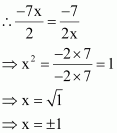 |
Also, common ratio =
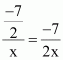
Thus, for x = ± 1, the given numbers will be in G.P.
![]()
Q7 :
Find the sum to 20 terms in the geometric progression 0.15, 0.015, 0.0015
Answer :
The given G.P. is 0.15, 0.015, 0.00015,
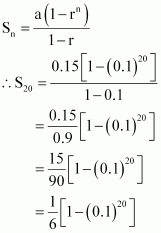 |
Here, a = 0.15 and
![]()
Q8 :
Find the sum to n terms
in the geometric progression ![]() Answer :
Answer :
The given G.P. is
![]()
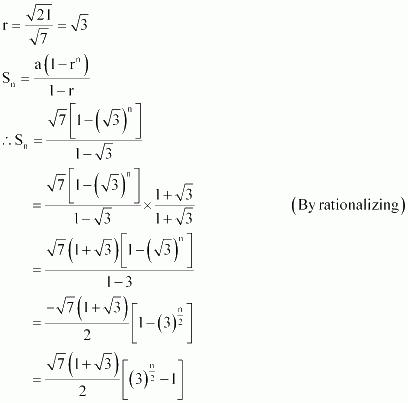 |
Here,
![]()
Q9 :
Find the sum to n terms in the geometric
progression ![]() Answer :
Answer :
The given G.P. is
![]()
Here, first term = a1 = 1 Common ratio = r = β a
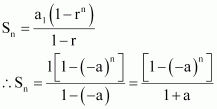
![]()
Q10 :
Find the sum to n terms
in the geometric progression ![]() Answer :
Answer :
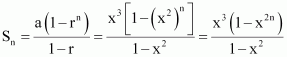 |
The given G.P. is
![]()
Q11 :
Evaluate ![]() Answer :
Answer :
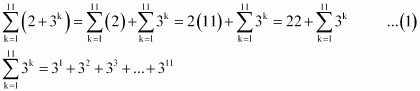
The terms of this sequence 3, 32, 33, forms a G.P.
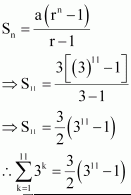
Substituting this value in equation (1), we obtain
![]()
Q12 :
The sum of first three terms of a
G.P. is ![]() and their product is 1. Find the
common ratio and the terms. Answer :
and their product is 1. Find the
common ratio and the terms. Answer :
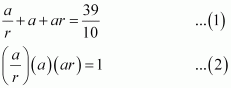 |
Let
From (2), we obtain
a3 = 1
⇒ a = 1 (Considering real roots only) Substituting a = 1 in equation (1), we obtain
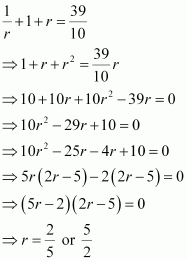
Q13 :
How many terms of G.P. 3, 32, 33, are needed to give the sum 120?
Answer :
The given G.P. is 3, 32, 33,
Let n terms of this G.P. be required to obtain the sum as 120.
Here, a = 3 and r = 3
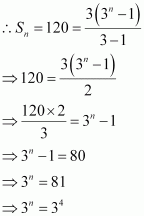
∴ n = 4
Thus, four terms of the given G.P. are required to obtain the sum as 120.
![]()
Q14 :
The sum of first three terms of a G.P. is 16 and the sum of the next three terms is 128. Determine the first term, the common ratio and the sum to n terms of the G.P.
Answer :
Let the G.P. be a, ar, ar2, ar3, According to the given condition,
a + ar + ar2 = 16 and ar3 + ar4 + ar5 = 128
⇒ a (1 + r + r2) = 16 (1)
ar3(1 + r + r2) = 128 (2)
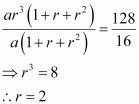 |
Dividing equation (2) by (1), we obtain
Substituting r = 2 in (1), we obtain
a (1 + 2 + 4) = 16
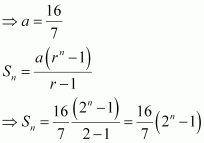 |
⇒ a (7) = 16
![]()
Q15 :
Given a G.P. with a = 729 and 7th term 64, determine S7.
Answer :
a = 729
a7 = 64
Let r be the common ratio of the G.P.
It is known that, an = a rnβ1 a7 = ar7β1 = (729)r6
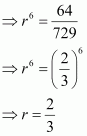 |
⇒ 64 = 729 r6
Also, it is
known that, ![]()
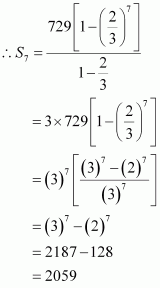
![]()
Q16 :
Find a G.P. for which sum of the first two terms is -4 and the fifth term is 4 times the third term.
Answer :
![]() Let a be the first term and
r be the common ratio of the G.P. According
to the given conditions,
Let a be the first term and
r be the common ratio of the G.P. According
to the given conditions,
a5 = 4 Χ a3
ar4 = 4ar2
⇒ r2 = 4
∴ r = ± 2
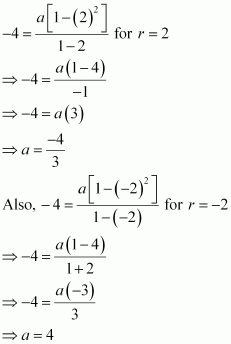 |
From (1), we obtain
Thus, the required G.P. is
Q17 :
If the 4th, 10th and 16th terms of a G.P. are x, y and z, respectively. Prove that x, y, z are in G.P.
Answer :
Let a be the first term and r be the common ratio of the G.P. According to the given condition,
a4 = a r3 = x (1) a10 = a r9 = y (2) a16= a r15 = z (3)
Dividing (2) by (1), we obtain
Dividing (3) by (2), we obtain
![]()
![]() ∴
∴
Thus, x, y, z are in G. P.
Q18 :
Find the sum to n terms of the sequence, 8, 88, 888, 8888
Answer :
The given sequence is 8, 88, 888, 8888
This sequence is not a G.P. However, it can be changed to G.P. by writing the terms as
Sn = 8 + 88 + 888 + 8888 +....................... to n terms
 |
Q19 :
Find the sum of the products
of the corresponding terms of the sequences
2, 4, 8, 16, 32 and 128, 32, 8, 2, ![]()
.
Answer :
![]() Here, 4, 2, 1, is
a G.P. First term, a = 4
Here, 4, 2, 1, is
a G.P. First term, a = 4
Common ratio, r = ![]()
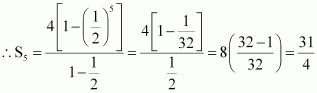 |
It is known that,
∴Required sum =
![]()
![]()
Q20 :
![]() Show that the products
of the corresponding terms of the
Show that the products
of the corresponding terms of the
sequences form a G.P, and find the common ratio.
Answer :
It has to be proved that the sequence, aA, arAR, ar2AR2, arnβ1ARnβ1, forms a G.P.
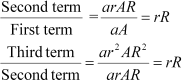 |
Thus, the above sequence forms a G.P. and the common ratio is rR.
Q21 :
Find four numbers forming a geometric progression in which third term is greater than the first term by 9, and the second term is greater than the 4th by 18.
Answer :
Let a be the first term and r be the common ratio of the G.P.
a1 = a, a2 = ar, a3 = ar2, a4 = ar3
By the given condition,
a3 = a1 + 9
⇒ ar2 = a + 9 (1)
a2 = a4 + 18
⇒ ar = ar3 + 18 (2)
From (1) and (2), we obtain
a(r2 β 1) = 9 (3)
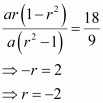 ar (1β r2)
= 18
(4) Dividing (4) by (3), we
obtain
ar (1β r2)
= 18
(4) Dividing (4) by (3), we
obtain
Substituting the value of r in (1), we obtain 4a = a + 9
⇒ 3a = 9
∴ a = 3
Thus, the first four numbers of the G.P. are 3, 3(β 2), 3(β2)2, and 3 (β2)3 i.e., 3 Έβ6, 12, and β24.
Q22 :
If the ![]() terms of a G.P. are a,
b and c, respectively. Prove that
terms of a G.P. are a,
b and c, respectively. Prove that ![]() Answer :
Answer :
Let A be the first term and R be the common ratio of the G.P. According to the given information,
ARp-1 = a ARq-1 = b ARr-1 = c
aq-rbr-p cp-q
= Aq-r x R(p-1) (q-r) x Ar-p x R(q-1) (r-p) x Ap-q x R(r -1)(p-q)
= Aq - r + r - p + p - q x R (pr- pr - q+ r) + (rq- r + p- pq) + (pr- p - qr+ q)
= A0 x R0
= 1
Thus, the given result is proved.
Q23 :
If the first and the nth term of a G.P. are a ad b, respectively, and if P is the product of n terms, prove that P2= (ab)n.
Answer :
The first term of the G.P is a and the last term is b.
Therefore, the G.P. is a, ar, ar2, ar3, arnβ1, where r is the common ratio.
b = arnβ1 (1)
P = Product of n terms
= (a) (ar) (ar2) (arnβ1)
= (a Χ a Χ a) (r Χ r2 Χ rnβ1)
= an r 1 + 2 + (nβ1) (2)
Here, 1, 2, (n β 1) is an A.P.
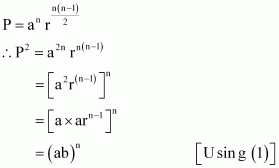 |
∴1 + 2 + .+ (n β 1)
Thus, the given result is proved.
![]()
Q24 :
Show that the ratio of the sum of
first n terms of a G.P.
to the sum of terms
from ![]() .
.
Answer :
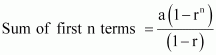 |
Let a be the first term and r be the common ratio of the G.P.
Since there are n terms from (n +1)th to (2n)th term,
Sum of terms from(n + 1)th to (2n)th
term 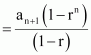
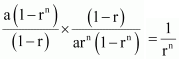 a n +1 = ar n + 1 β 1 = arn
a n +1 = ar n + 1 β 1 = arn
Thus, required ratio =
Thus, the ratio of the sum of first n terms of a G.P. to the sum of terms from (n + 1)th to (2n)th term is
Q25 :
If a, b, c and
d are in G.P. show that ![]() .
.
Answer :
a, b, c, d are in G.P. Therefore,
bc = ad (1) b2 = ac (2) c2 = bd (3)
It has to be proved that,
(a2 + b2 + c2) (b2 + c2 + d2) = (ab + bc β cd)2
R.H.S.
= (ab + bc + cd)2
= (ab + ad + cd)2 [Using (1)]
= [ab + d (a + c)]2
= a2b2 + 2abd (a + c) + d2 (a + c)2
= a2b2 +2a2bd + 2acbd + d2(a2 + 2ac + c2)
= a2b2 + 2a2c2 + 2b2c2 + d2a2 + 2d2b2 + d2c2 [Using (1) and (2)]
= a2b2 + a2c2 + a2c2 + b2c2 + b2c2 + d2a2 + d2b2 + d2b2 + d2c2
= a2b2 + a2c2 + a2d2 + b2 Χ b2 + b2c2 + b2d2 + c2b2 + c2 Χ c2 + c2d2
[Using (2) and (3) and rearranging terms]
= a2(b2 + c2 + d2) + b2 (b2 + c2 + d2) + c2 (b2+ c2 + d2)
= (a2 + b2 + c2) (b2 + c2 + d2)
= L.H.S.
∴ L.H.S. = R.H.S.
∴
Q26 :
Insert two numbers between 3 and 81 so that the resulting sequence is G.P.
Answer :
Let G1 and G2 be two numbers between 3 and 81 such that the series, 3, G1, G2, 81, forms a G.P. Let a be the first term and r be the common ratio of the G.P.
∴81 = (3) (r)3
⇒ r3 = 27
∴ r = 3 (Taking real roots only) For r = 3,
G1 = ar = (3) (3) = 9
G2 = ar2 = (3) (3)2 = 27
Thus, the required two numbers are 9 and 27.
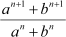 Q27 :
Q27 :
Find the value of n so that may be the geometric mean between a and b.
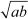 Answer :
Answer :
G. M. of a and b is .
![]() By the given condition, Squaring
both sides, we obtain
By the given condition, Squaring
both sides, we obtain
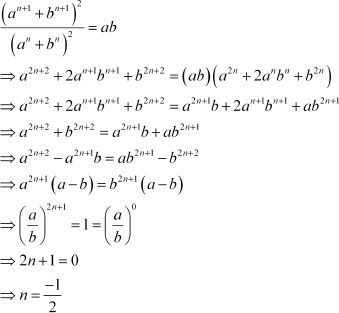
Q28 :
![]() The sum of two numbers is 6 times their geometric mean, show that numbers are in the ratio
The sum of two numbers is 6 times their geometric mean, show that numbers are in the ratio
.
Answer :
![]() Let the two numbers be
a and b.
Let the two numbers be
a and b.
G.M. =
According to the given condition,
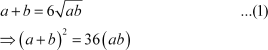 |
Also,
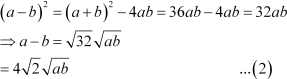 |
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
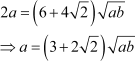
Substituting the value of a in (1), we obtain
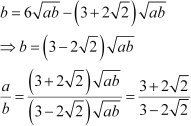 |
Q29 :
![]() If A and G be
A.M. and G.M., respectively between
two positive numbers,
prove that the numbers are
If A and G be
A.M. and G.M., respectively between
two positive numbers,
prove that the numbers are
.
Answer :
It is given that A and G are A.M. and G.M. between two positive numbers. Let these two positive numbers be a and b.
 |
From (1) and (2), we obtain
a + b = 2A (3)
ab = G2 (4)
Substituting the value of a and b from (3) and (4) in the identity (a β b)2 = (a + b)2 β 4ab, we obtain (a β b)2 = 4A2 β 4G2 = 4 (A2βG2)
(a β b)2 = 4 (A + G) (A β G)
From (3) and (5), we obtain
Substituting the value of a in (3), we obtain
![]()
![]() Thus, the two numbers are .
Thus, the two numbers are .
Q30 :
The number of bacteria in a certain culture doubles every hour. If there were 30 bacteria present in the culture originally, how many bacteria will be present at the end of 2nd hour, 4th hour and nth hour?
Answer :
It is given that the number of bacteria doubles every hour. Therefore, the number of bacteria after every hour will form a G.P.
Here, a = 30 and r = 2
∴ a3 = ar2 = (30) (2)2 = 120
Therefore, the number of bacteria at the end of 2nd hour will be 120.
a5 = ar4 = (30) (2)4 = 480
The number of bacteria at the end of 4th hour will be 480.
an +1 = arn = (30) 2n
Thus, number
of bacteria at the end of nth hour will be 30(2)n.
Q31 :
What will Rs 500 amounts to in 10 years after its deposit in a bank which pays annual interest rate of 10% compounded annually?
Answer :
The amount deposited in the bank is Rs 500.
At the end of first year, amount = ![]() = Rs 500
(1.1) At the end of 2nd year, amount = Rs 500 (1.1) (1.1)
= Rs 500
(1.1) At the end of 2nd year, amount = Rs 500 (1.1) (1.1)
At the end of 3rd year, amount = Rs 500 (1.1) (1.1) (1.1) and so on
∴Amount at the end of 10 years = Rs 500 (1.1) (1.1) (10 times)
= Rs 500(1.1)10
Q32 :
If A.M. and G.M. of roots of a quadratic equation are 8 and 5, respectively, then obtain the quadratic equation.
Answer :
Let the root of the quadratic equation be a and b. According to the given condition,
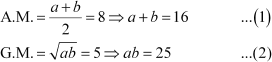
The quadratic equation is given by,
x2β x (Sum of roots) + (Product of roots) = 0
x2 β x (a + b) + (ab) = 0
x2 β 16x + 25 = 0 [Using (1) and (2)]
Thus, the required
quadratic equation is x2 β 16x + 25 = 0
Exercise 9.4 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 196
Q1 :
Find the sum to n terms of the series 1 x 2 + 2 x 3 + 3 x 4 + 4 x 5 +
Answer :
The given series is 1 Χ 2 + 2 Χ 3 + 3 Χ 4 + 4 Χ 5 +
nth term, an = n ( n + 1)
Q2 :
Find the sum to n terms of the series 1 x 2 x 3 + 2 x 3 x 4 + 3 x 4 x 5 +
Answer :
The given series is 1 Χ 2 Χ 3 + 2 Χ 3 Χ 4 + 3 Χ 4 Χ 5 +
nth term, an = n ( n + 1) ( n + 2)
= (n2 + n) (n + 2)
= n3 + 3n2 + 2n
Q3 :
Find the sum to n terms of the series 3 x 12 + 5 x 22 + 7 x 32 +
Answer :
The given series is 3 Χ12 + 5 Χ 22 + 7 Χ 32 +
nth term, an = ( 2n + 1) n2 = 2n3 + n2
Q4 :
Find the sum to n terms of each of the series in Exercises 1 to 7. 3 x 12 + 5 x 22 + 7 x 32 +
Answer :
The given series is 3 Χ12 + 5 Χ 22 + 7 Χ 32 +
nth term, an = ( 2n + 1) n2 = 2n3 + n2
 Q5 :
Q5 :
Find the sum to n terms of the series
Answer :
![]()
![]()
![]() The given series
is
The given series
is
nth term, an =
Adding the above terms column wise, we obtain
Q6 :
![]() Find the sum to n terms of the series
Find the sum to n terms of the series
Answer :
The given series is 52 + 62 + 72 + + 202
nth term, an = ( n + 4)2 = n2 + 8n + 16
16th term is (16 + 4)2 = 2022
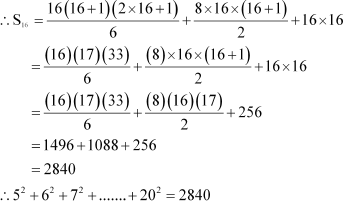
Q7 :
Find the sum to n terms of the series 3 x 8 + 6 x 11 + 9 x 14 +
Answer :
The given series is 3 Χ 8 + 6 Χ 11 + 9 Χ 14 +
an = (nth term of 3, 6, 9 ) Χ (nth term of 8, 11, 14, )
= (3n) (3n + 5)
= 9n2 + 15n
Q8 :
Find the sum to n terms of the series 12 + (12 + 22) + (12 + 22 + 32) +
Answer :
The given series is 12 + (12 + 22) + (12 + 22 + 32 ) +
an = (12 + 22 + 32 + .+ n2)
= n(n+1)(2n+1)6=n(2n2+3n+1)6=2n3+3n2+n6=13n3+12n2+16n
Q9 :
Find the sum to n terms of the series whose nth term is given by n (n + 1) (n + 4).
Answer :
an = n (n + 1) (n + 4) = n(n2 + 5n + 4) = n3 + 5n2 + 4n
Q10 :
Find the sum to n terms of the series whose nth terms is given by n2 + 2n
Answer :
an= n2 + 2n
![]() Consider
Consider
The above series 2, 22, 23, is a G.P. with both the first term and common ratio equal to 2.
Therefore, from (1) and (2), we obtain
Q11 :
Find the sum to n terms of the series whose nth terms is given by (2n - 1)2
Answer :
an = (2n β 1)2 = 4n2 β 4n + 1
Exercise Miscellaneous : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 199
Q1 :
Show that the sum of (m + n)th and (m - n)th terms of an A.P. is equal to twice the mth term.
Answer :
Let a and d be the first term and the common difference of the A.P. respectively.
It is known that the kth term of an A. P. is given by
ak = a + (k -1) d
∴ am + n = a + (m + n -1) d am - n = a + (m - n -1) d am = a + (m -1) d
∴ am + n + am - n = a + (m + n -1) d + a + (m - n -1) d
= 2a + (m + n -1 + m - n -1) d
= 2a + (2m - 2) d
= 2a + 2 (m - 1) d
=2 [a + (m - 1) d]
= 2am
Thus, the sum of (m + n)th and (m - n)th terms of an A.P. is equal to
twice the mth term.
Q2 :
If the sum of three numbers in A.P., is 24 and their product is 440, find the numbers.
Answer :
Let the three numbers in A.P. be a - d, a, and a + d. According to the given information,
(a - d) + (a) + (a + d) = 24 (1)
⇒ 3a = 24
∴ a = 8
(a - d) a (a + d) = 440 (2)
⇒ (8 - d) (8) (8 + d) = 440
⇒ (8 - d) (8 + d) = 55
⇒ 64 - d2 = 55
⇒ d2 = 64 - 55 = 9
⇒ d = ± 3
Therefore, when d = 3, the numbers are 5, 8, and 11 and when d = -3, the numbers are 11, 8, and 5.
Thus, the three numbers are 5, 8, and 11.
Q3 :
Let the sum of n, 2n, 3n terms of an A.P. be S1, S2 and S3, respectively, show that S3 = 3 (S2- S1)
Answer :
Let a and b be the first term and the common difference of the A.P. respectively. Therefore,
From (1) and (2), we obtain
Hence, the given result is proved.
Q4 :
Find the sum of all numbers between 200 and 400 which are divisible by 7.
Answer :
The numbers lying between 200 and 400, which are divisible by 7, are 203, 210, 217, 399
∴First term, a = 203 Last term, l = 399
Common difference, d = 7
Let the number of terms of the A.P. be n.
∴ an = 399 = a + (n β1) d
⇒ 399 = 203 + (n β1) 7
⇒ 7 (n β1) = 196
⇒ n β1 = 28
⇒ n = 29
Thus, the
required sum is 8729.
Q5 :
Find the sum of integers from 1 to 100 that are divisible by 2 or 5.
Answer :
The integers from 1 to 100, which are divisible by 2, are 2, 4, 6 100.
This forms an A.P. with both the first term and common difference equal to 2.
⇒100 = 2 + (n β1) 2
⇒ n = 50
The integers from 1 to 100, which are divisible by 5, are 5, 10 100.
This forms an A.P. with both the first term and common difference equal to 5.
∴100 = 5 + (n β1) 5
⇒ 5n = 100
⇒ n = 20
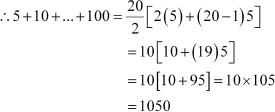
The integers, which are divisible by both 2 and 5, are 10, 20, 100.
This also forms an A.P. with both the first term and common difference equal to 10.
∴100 = 10 + (n β1) (10)
⇒ 100 = 10n
⇒ n = 10
∴Required sum = 2550 + 1050 β 550 = 3050
Thus, the sum of the integers from 1
to 100, which are divisible
by 2 or 5, is 3050.
Q6 :
Find the sum of all two digit numbers which when divided by 4, yields 1 as remainder.
Answer :
The two-digit numbers, which when divided by 4, yield 1 as remainder, are 13, 17, 97.
This series forms an A.P. with first term 13 and common difference 4. Let n be the number of terms of the A.P.
It is known that the nth term of an A.P. is given by, an = a + (n β1) d
∴97 = 13 + (n β1) (4)
⇒ 4 (n β1) = 84
⇒ n β 1 = 21
⇒ n = 22
Sum of n terms of an A.P. is given by,
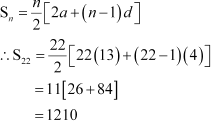
Thus, the
required sum is 1210.
 Q7 :
Q7 :
If f is a function satisfying such
that , find the value of n.
Answer :
It is given that,
f (x + y) = f (x) Χ f (y) for all x, y ∈ N (1)
f (1) = 3
Taking x = y = 1 in (1), we obtain
f (1 + 1) = f (2) = f (1) f (1) = 3 Χ 3 = 9
Similarly,
f (1 + 1 + 1) = f (3) = f (1 + 2) = f (1) f (2) = 3 Χ 9 = 27
f (4) = f (1 + 3) = f (1) f (3) = 3 Χ 27 = 81
∴ f (1), f (2), f (3), , that is 3, 9, 27, , forms a G.P. with both the first term and common ratio equal to 3.
It is known that, ![]() It is given that,
It is given that,
![]()
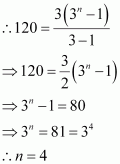
Thus, the
value of n is 4.
Q8 :
The sum of some terms of G.P. is 315 whose first term and the common ratio are 5 and 2, respectively. Find the last term and the number of terms.
Answer :
Let the sum of n terms of the G.P. be 315.
It is known
that, ![]()
It is given that the first term a is 5 and common ratio r is 2.
∴Last term of the G.P = 6th term = ar6 β 1 = (5)(2)5 = (5)(32) = 160 Thus, the last term of the G.P. is 160.
Q9 :
The first term of a G.P. is 1. The sum of the third term and fifth term is 90. Find the common ratio of G.P.
Answer :
Let a and r be the first term and the common ratio of the G.P. respectively.
∴ a = 1
a3 = ar2 = r2
a5 = ar4 = r4
∴ r2 + r4 = 90
⇒ r4 + r2 β 90 = 0
Thus, the common ratio of the G.P. is ±3.
Q10 :
The sum of three numbers in G.P. is 56. If we subtract 1, 7, 21 from these numbers in that order, we obtain an arithmetic progression. Find the numbers.
Answer :
Let the three numbers in G.P. be a, ar, and ar2. From the given condition, a + ar + ar2 = 56
⇒ a (1 + r + r2) = 56
![]() (1)
(1)
a β 1, ar β 7, ar2 β 21 forms an A.P.
∴(ar β 7) β (a β 1) = (ar2 β 21) β (ar β 7)
⇒ ar β a β 6 = ar2 β ar β 14
⇒ar2 β 2ar + a = 8
⇒ar2 β ar β ar + a = 8
⇒a(r2 + 1 β 2r) = 8
⇒ a (r β 1)2 = 8 (2)
⇒7(r2 β 2r + 1) = 1 + r + r2
⇒7r2 β 14 r + 7 β 1 β r β r2 = 0
⇒ 6r2 β 15r + 6 = 0
⇒ 6r2 β 12r β 3r + 6 = 0
⇒ 6r (r β 2) β 3 (r β 2) = 0
⇒ (6r β 3) (r β 2) = 0
![]()
When r = 2, a = 8
When ![]()
Therefore, when r = 2, the three numbers in G.P. are 8, 16, and 32.
When ![]() , the three numbers in G.P. are
32, 16, and 8.
, the three numbers in G.P. are
32, 16, and 8.
Thus, in either case, the three
required numbers are 8, 16, and
32.
Q11 :
A G.P. consists of an even number of terms. If the sum of all the terms is 5 times the sum of terms occupying odd places, then find its common ratio.
Answer :
Let the G.P. be T1, T2, T3, T4, T2n. Number of terms = 2n
According to the given condition,
T1 + T2 + T3 + + T2n = 5 [T1 + T3 + +T2nβ1]
⇒ T1 + T2 + T3 + + T2n β 5 [T1 + T3 + + T2nβ1] = 0
⇒ T2 + T4 + + T2n = 4 [T1 + T3 + + T2nβ1]
Let the G.P. be a, ar, ar2, ar3,
Thus, the common
ratio of the G.P.
is 4.
Q12 :
The sum of the first four terms of an A.P. is 56. The sum of the last four terms is 112. If its first term is 11, then find the number of terms.
Answer :
Let the A.P. be a, a + d, a + 2d, a + 3d, ... a + (n - 2) d, a + (n - 1)d.
Sum of first four terms = a + (a + d) + (a + 2d) + (a + 3d) = 4a + 6d Sum of last four terms = [a + (n - 4) d] + [a + (n - 3) d] + [a + (n - 2) d]
+ [a + n - 1) d]
= 4a + (4n - 10) d
According to the given condition, 4a + 6d = 56
⇒ 4(11) + 6d = 56 [Since a = 11 (given)]
⇒ 6d = 12
⇒ d = 2
∴ 4a + (4n -10) d = 112
⇒ 4(11) + (4n - 10)2 = 112
⇒ (4n - 10)2 = 68
⇒ 4n - 10 = 34
⇒ 4n = 44
⇒ n = 11
Thus, the number of terms of the A.P.
is 11.
 Q13 :
Q13 :
If , then show that a, b, c and d are in G.P.
Answer :
It is given that,
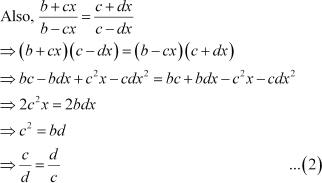
From (1) and (2), we obtain
Thus, a, b, c, and d are in G.P.
Q14 :
Let S be the sum, P the product and R the sum of reciprocals of n terms in a G.P. Prove that P2Rn = Sn
Answer :
Let the G.P. be a, ar, ar2, ar3, arnβ 1 According to the given information,

Hence, P2 Rn
= Sn
Q15 :
![]() The pth, qth and rth terms of an A.P. are a, b, c respectively. Show that
The pth, qth and rth terms of an A.P. are a, b, c respectively. Show that
Answer :
Let t and d be the first term and the common difference of the A.P. respectively. The nth term of an A.P. is given by, an = t + (n β 1) d
Therefore,
ap = t + (p β 1) d = a (1) aq = t + (q β 1)d = b (2) ar = t + (r β 1) d = c (3)
Subtracting equation (2) from (1), we obtain (p β 1 β q + 1) d = a β b
⇒ (p β q) d = a β b
Subtracting equation (3) from (2), we obtain (q β 1 β r + 1) d = b β c
⇒ (q βr) d = b β c
Equating both the values of d obtained in (4) and (5), we obtain
Thus, the given result
is proved.
 Q16 :
Q16 :
If a are in A.P., prove that a, b, c are in A.P.
 Answer :
Answer :
It is given that a are in A.P.
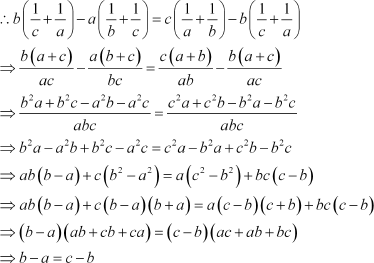
Thus, a, b, and c are in A.P.
Q17 :
If a, b,c, d
are in G.P, prove that ![]() are in G.P. Answer :
are in G.P. Answer :
It is given that a, b, c,and d are in G.P.
∴b2 = ac (1) c2 = bd (2) ad = bc (3)
It has to be proved that (an + bn), (bn + cn), (cn + dn) are in G.P. i.e., (bn + cn)2 = (an + bn) (cn + dn)
Consider L.H.S.
(bn + cn)2 = b2n + 2bncn + c2n
= (b2)n+ 2bncn + (c2) n
= (ac)n + 2bncn + (bd)n [Using (1) and (2)]
= an cn + bncn+ bn cn + bn dn
= an cn + bncn+ an dn + bn dn [Using (3)]
= cn (an + bn) + dn (an + bn)
= (an + bn) (cn + dn)
= R.H.S.
∴ (bn + cn)2 = (an + bn) (cn + dn)
Thus, (an + bn), (bn + cn), and (cn + dn) are in G.P.
Q18 :
![]()
![]() If a and b are the roots of are roots
of , where a, b,
c, d, form a
If a and b are the roots of are roots
of , where a, b,
c, d, form a
G.P. Prove that (q + p): (q β p) = 17:15.
Answer :
It is given that a and b are the roots of x2 β 3x + p = 0
∴ a + b = 3 and ab = p (1)
![]() Also, c and d are the roots of
Also, c and d are the roots of
∴c + d = 12 and cd = q (2)
It is given that a, b, c, d are in G.P. Let a = x, b = xr, c = xr2, d = xr3 From (1) and (2), we obtain
x + xr = 3
⇒ x (1 + r) = 3
xr2 + xr3 =12
⇒ xr2 (1 + r) = 12
On dividing, we obtain
Case I:
When r = 2 and x =1,
ab = x2r = 2
cd = x2r5 = 32
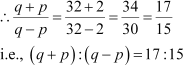
Case II:
When r = β2, x = β3,
ab = x2r = β18
cd = x2r5 = β 288
Thus, in both the
cases, we obtain (q + p): (q β p) = 17:15
Q19 :
![]() The ratio of the A.M and G.M. of two positive numbers
a and b, is m:n. Show
that .
The ratio of the A.M and G.M. of two positive numbers
a and b, is m:n. Show
that .
Answer :
![]() Let the two numbers
be a and b.
Let the two numbers
be a and b.
![]() A.M and G.M. = According
to the given condition,
A.M and G.M. = According
to the given condition,
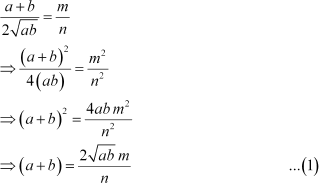
Using this in the identity (a β b)2 = (a + b)2 β 4ab, we obtain
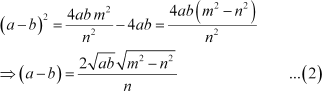
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Substituting the value of a in (1), we obtain
 Q20 :
Q20 :
If a, b, c are in A.P,; b, c, d are in G.P and are in A.P. prove that a, c, e are in G.P.
Answer :
It is given that a, b, c are in A.P.
∴ b β a = c β b (1)
It is given that b, c, d, are in G.P.
![]() ∴ c2 = bd
(2)
∴ c2 = bd
(2)
Also, are in A.P.

It has to be proved that a, c, e are in G.P. i.e., c2 = ae
From (1), we obtain
From (2), we obtain
Substituting these values in (3), we obtain
Thus, a, c, and e are in G.P.
Q21 :
Find the sum of the following series up to n terms: (i) 5 + 55 + 555 + (ii) .6 +.66 +. 666 +
Answer :
(i) 5 + 55 + 555 +
Let Sn = 5 + 55 + 555 + .. to n terms
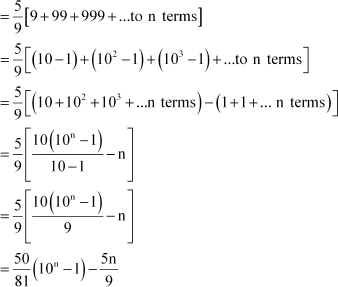
(ii) .6 +.66 +. 666 +
Let Sn = 06. + 0.66 + 0.666 + to n terms
Q22 :
Find the 20th term of the series 2 x 4 + 4 x 6 + 6 x 8 + + n terms.
Answer :
The given series is 2 x 4 + 4 x 6 + 6 x 8 + n terms
∴ nth term = an = 2n x (2n + 2) = 4n2 + 4n
a20 = 4 (20)2 + 4(20) = 4 (400) + 80 = 1600 + 80 = 1680
Thus, the 20th term of the series is
1680.
Q23 :
Find the sum of the first n terms of the series: 3 + 7 + 13 + 21 + 31 +
Answer :
The given series is 3 + 7 + 13 + 21 + 31 +
S = 3 + 7 + 13 + 21 + 31 + + anβ1 + an
S = 3 + 7 + 13 + 21 + . + an β 2 + an β 1 + an
On subtracting both the equations, we obtain
S β S = [3 + (7 + 13 + 21 + 31 + + anβ1 + an)] β [(3 + 7 + 13 + 21 + 31 + + anβ1) + an]
S β S = 3 + [(7 β 3) + (13 β 7) + (21 β 13) + + (an β anβ1)] β an
0 = 3 + [4 + 6 + 8 + (n β1) terms] β an an = 3 + [4 + 6 + 8 + (n β1) terms]
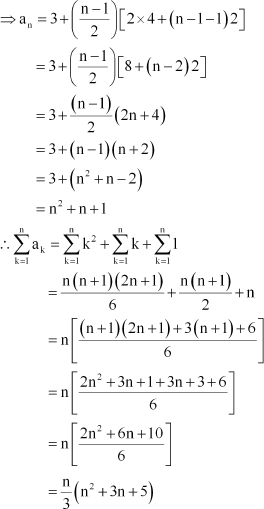
Q24 :
![]() If S1, S2, S3 are
the sum of first n natural numbers, their squares and their cubes,
respectively, show that
If S1, S2, S3 are
the sum of first n natural numbers, their squares and their cubes,
respectively, show that
Answer :
From the given information,
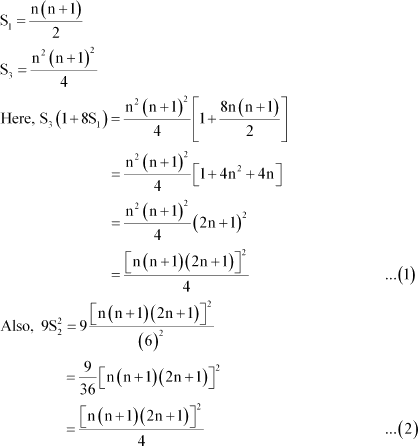
![]() Thus, from (1) and (2), we obtain
Thus, from (1) and (2), we obtain
 Q25 :
Q25 :
Find the sum of the following series up to n terms:
 Answer :
Answer :
The nth term of the given series is
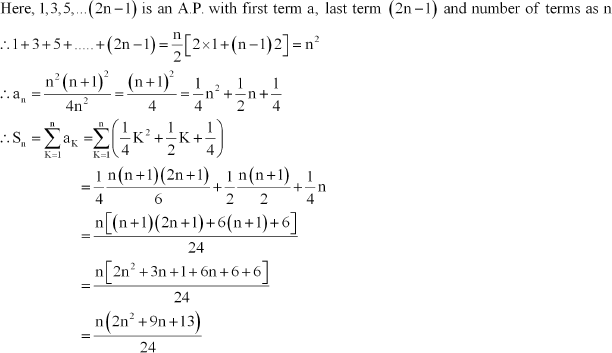
 Q26 :
Q26 :
Show that
Answer :
nth term of the numerator = n(n + 1)2 = n3 + 2n2 + n nth term of the denominator = n2(n + 1) = n3 + n2
![]()
From (1), (2), and (3), we obtain
Thus, the given result is proved.
Q27 :
A farmer buys a used tractor for Rs 12000. He pays Rs 6000 cash and agrees to pay the balance in annual installments of Rs 500 plus 12% interest on the unpaid amount. How much will be the tractor cost him?
Answer :
It is given that the farmer pays Rs 6000 in cash.
Therefore, unpaid amount = Rs 12000 β Rs 6000 = Rs 6000 According to the given condition, the interest paid annually is 12% of 6000, 12% of 5500, 12% of 5000, , 12% of 500
Thus, total interest to be paid = 12% of 6000 + 12% of 5500 + 12% of 5000 + + 12% of 500
= 12% of (6000 + 5500 + 5000 + + 500)
= 12% of (500 + 1000 + 1500 + + 6000)
Now, the series 500, 1000, 1500 6000 is an A.P. with both the first term and common difference equal to 500. Let the number of terms of the A.P. be n.
∴ 6000 = 500 + (n β 1) 500
⇒ 1 + (n β 1) = 12
![]() ⇒ n = 12
⇒ n = 12
∴Sum of the A.P
Thus, total interest to be paid = 12% of (500 + 1000 + 1500 + + 6000)
= 12% of 39000 = Rs 4680
Thus, cost
of tractor = (Rs 12000 + Rs 4680) = Rs 16680
Q28 :
Shamshad Ali buys a scooter for Rs 22000. He pays Rs 4000 cash and agrees to pay the balance in annual installment of Rs 1000 plus 10% interest on the unpaid amount. How much will the scooter cost him?
Answer :
It is given that Shamshad Ali buys a scooter for Rs 22000 and pays Rs 4000 in cash.
∴Unpaid amount = Rs 22000 β Rs 4000 = Rs 18000 According to the given condition, the interest paid annually is 10% of 18000, 10% of 17000, 10% of 16000 10% of 1000
Thus, total interest to be paid = 10% of 18000 + 10% of 17000 + 10% of 16000 + + 10% of 1000
= 10% of (18000 + 17000 + 16000 + + 1000)
= 10% of (1000 + 2000 + 3000 + + 18000)
Here, 1000, 2000, 3000 18000 forms an A.P. with first term and common difference both equal to 1000. Let the number of terms be n.
∴ 18000 = 1000 + (n β 1) (1000)
⇒ n = 18
∴ Total interest paid = 10% of (18000 + 17000 + 16000 + + 1000)
= 10% of Rs 171000 = Rs 17100
∴Cost of scooter =
Rs 22000 + Rs 17100 = Rs 39100
Q29 :
A person writes a letter to four of his friends. He asks each one of them to copy the letter and mail to four different persons with instruction that they move the chain similarly. Assuming that the chain is not broken and that it costs 50 paise to mail one letter. Find the amount spent on the postage when 8th set of letter is mailed.
Answer :
The numbers of letters mailed forms a G.P.: 4, 42, 48 First term = 4
Common ratio = 4 Number of terms = 8
It is known that the sum of n terms of a G.P. is given by
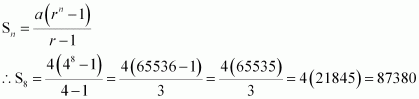
It is given that the cost to mail one letter is 50 paisa.
∴Cost of mailing 87380 letters ![]() = Rs
43690 Thus, the amount spent when 8th set of letter
is mailed is Rs 43690.
= Rs
43690 Thus, the amount spent when 8th set of letter
is mailed is Rs 43690.
Q30 :
A man deposited Rs 10000 in a bank at the rate of 5% simple interest annually. Find the amount in 15th year since he deposited the amount and also calculate the total amount after 20 years.
Answer :
![]() It is given that the man deposited Rs 10000 in a bank at the rate of 5%
simple interest annually.
It is given that the man deposited Rs 10000 in a bank at the rate of 5%
simple interest annually.
![]() ∴ Interest in first year
∴ Interest in first year
∴Amount in 15th year = Rs
= Rs 10000 + 14 Χ Rs 500
= Rs 10000 + Rs 7000
![]() = Rs 17000
= Rs 17000
Amount after 20 years =
= Rs 10000 + 20 Χ Rs 500
= Rs 10000 + Rs 10000
= Rs 20000
Q31 :
A manufacturer reckons that the value of a machine, which costs him Rs 15625, will depreciate each year by 20%. Find the estimated value at the end of 5 years.
Answer :
Cost of machine = Rs 15625
![]() Machine depreciates by 20% every year.
Machine depreciates by 20% every year.
![]() Therefore, its
value after every year is 80%
of the original cost i.e., of the original cost.
Therefore, its
value after every year is 80%
of the original cost i.e., of the original cost.
∴ Value at the end of 5 years = = 5 Χ 1024 = 5120 Thus, the value of the machine at the end of 5 years is Rs 5120.
Q32 :
150 workers were engaged to finish a job in a certain number of days. 4 workers dropped out on second day, 4 more workers dropped out on third day and so on. It took 8 more days to finish the work. Find the number of days in which the work was completed.
Answer :
Let x be the number of days in which 150 workers finish the work. According to the given information,
150x = 150 + 146 + 142 + . (x + 8) terms
The series 150 + 146 + 142 + . (x + 8) terms is an A.P. with first term 146, common difference β4 and number of terms as (x + 8)
However, x cannot be negative.
∴x = 17
Therefore, originally, the number of days in which the work was completed is 17. Thus, required number of days = (17 + 8) = 25