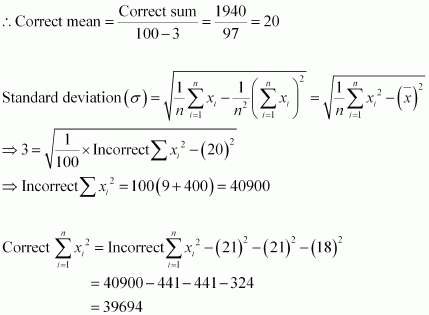Statistics
NCERT Textbook Solution (Laptop/Desktop is best to view this page)
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 15
Statistics Class 11
Chapter 15 Statistics Exercise 15.1, 15.2, 15.3, miscellaneous Solutions
Exercise 15.1 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 360
Q1 :
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 17
Answer :
The given data is
4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 17
Mean of the data, ![]()
The deviations of the respective observations from the
mean ![]() are β6, β 3, β2, β1, 0, 2,
3, 7
are β6, β 3, β2, β1, 0, 2,
3, 7
The absolute values of
the deviations, i.e. ![]() , are 6, 3, 2, 1, 0, 2, 3, 7
, are 6, 3, 2, 1, 0, 2, 3, 7
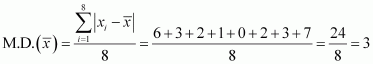 |
The required mean deviation about the mean is
![]()
Q2 :
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data 38, 70, 48, 40, 42, 55, 63, 46, 54, 44
Answer :
The given data is
38, 70, 48, 40, 42, 55, 63, 46, 54, 44
Mean of the given data,
![]()
![]() The deviations of the respective observations from the mean are β12, 20, β2, β10, β8, 5, 13,
β4, 4, β6
The deviations of the respective observations from the mean are β12, 20, β2, β10, β8, 5, 13,
β4, 4, β6
The absolute values of
the deviations, i.e. ![]() , are 12, 20, 2, 10, 8, 5, 13, 4, 4, 6
, are 12, 20, 2, 10, 8, 5, 13, 4, 4, 6
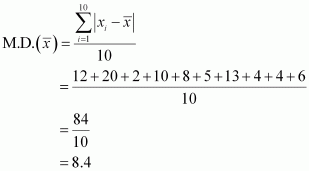 |
The required mean deviation about the mean is
![]()
Q3 :
Find the mean deviation about the median for the data. 13, 17, 16, 14, 11, 13, 10, 16, 11, 18, 12, 17
Answer :
The given data is
13, 17, 16, 14, 11, 13, 10, 16, 11, 18, 12, 17
Here, the numbers of observations are 12, which is even. Arranging the data in ascending order, we obtain
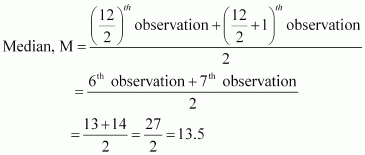 |
10, 11, 11, 12, 13, 13, 14, 16, 16, 17, 17, 18
The deviations of the respective observations from the median, i.e. ![]() are
are
β3.5, β2.5, β2.5, β1.5, β0.5, β0.5, 0.5, 2.5, 2.5, 3.5, 3.5, 4.5
The absolute values of
the deviations, ![]() , are 3.5,
2.5, 2.5, 1.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 2.5,
2.5, 3.5, 3.5, 4.5
, are 3.5,
2.5, 2.5, 1.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 2.5,
2.5, 3.5, 3.5, 4.5
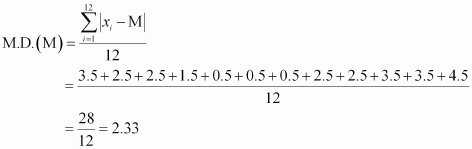 |
The required mean deviation about the median is
![]()
Q4 :
Find the mean deviation about the median for the data 36, 72, 46, 42, 60, 45, 53, 46, 51, 49
Answer :
The given data is
36, 72, 46, 42, 60, 45, 53, 46, 51, 49
Here, the number of observations is 10, which is even. Arranging the data in ascending order, we obtain
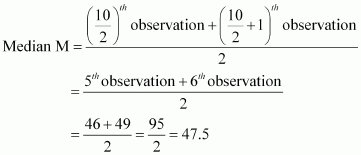 |
36, 42, 45, 46, 46, 49, 51, 53, 60, 72
The deviations of the respective observations from the
median, i.e. ![]() are β11.5, β5.5, β2.5, β1.5, β1.5, 1.5, 3.5,
5.5, 12.5, 24.5
are β11.5, β5.5, β2.5, β1.5, β1.5, 1.5, 3.5,
5.5, 12.5, 24.5
The absolute values of
the deviations, ![]() , are 11.5, 5.5, 2.5, 1.5, 1.5,
1.5, 3.5, 5.5, 12.5, 24.5
, are 11.5, 5.5, 2.5, 1.5, 1.5,
1.5, 3.5, 5.5, 12.5, 24.5
Thus, the required mean deviation about the median is
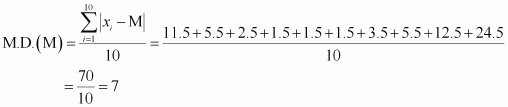
Q5 :
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data.
|
xi |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
|
fi |
7 |
4 |
6 |
3 |
5 |
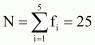 Answer :
Answer :
|
xi |
fi |
fi xi |
|
|
|
5 |
7 |
35 |
9 |
63 |
|
10 |
4 |
40 |
4 |
16 |
|
15 |
6 |
90 |
1 |
6 |
|
20 |
3 |
60 |
6 |
18 |
|
25 |
5 |
125 |
11 |
55 |
|
|
25 |
350 |
|
158 |
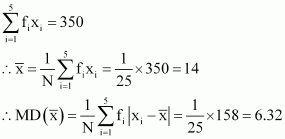 |
![]()
Q6 :
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data
|
xi |
10 |
30 |
50 |
70 |
90 |
|
fi |
4 |
24 |
28 |
16 |
8 |
Answer :
|
xi |
fi |
fi xi |
|
|
|
10 |
4 |
40 |
40 |
160 |
|
30 |
24 |
720 |
20 |
480 |
|
50 |
28 |
1400 |
0 |
0 |
|
70 |
16 |
1120 |
20 |
320 |
|
90 |
8 |
720 |
40 |
320 |
|
|
80 |
4000 |
|
1280 |
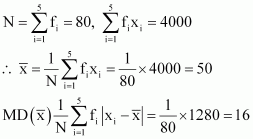 Q7 :
Q7 :
Find the mean deviation about the median for the data.
|
xi |
5 |
7 |
9 |
10 |
12 |
15 |
|
fi |
8 |
6 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
6 |
Answer :
The given observations are already in ascending order.
Adding a column corresponding to cumulative frequencies of the given data, we obtain the following table.
|
xi |
fi |
c.f. |
|
5 |
8 |
8 |
|
7 |
6 |
14 |
|
9 |
2 |
16 |
|
10 |
2 |
18 |
|
12 |
2 |
20 |
|
15 |
6 |
26 |
Here, N = 26, which is even.
Median is the mean of 13th and 14th observations. Both of these observations lie in the cumulative frequency 14, for which the corresponding observation is 7.
The absolute
values of the deviations from median, i.e. ![]() are
are
|
|xi β M| |
2 |
0 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
8 |
|
fi |
8 |
6 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
6 |
|
fi |xi β M| |
16 |
0 |
4 |
6 |
10 |
48 |
![]()
Q8 :
Find the mean deviation about the median for the data
|
xi |
15 |
21 |
27 |
30 |
35 |
|
fi |
3 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
Answer :
The given observations are already in ascending order.
Adding a column corresponding to cumulative frequencies of the given data, we obtain the following table.
|
xi |
fi |
c.f. |
|
15 |
3 |
3 |
|
21 |
5 |
8 |
|
27 |
6 |
14 |
|
30 |
7 |
21 |
|
35 |
8 |
29 |
![]() Here, N = 29, which is odd.
Here, N = 29, which is odd.
observation = 15th observation
This observation lies in the cumulative frequency 21, for which the corresponding observation is 30.
∴ Median = 30
The absolute
values of the deviations from median, i.e. ![]() are
are
|
|xi β M| |
15 |
9 |
3 |
0 |
5 |
|
fi |
3 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
|
fi |xi β M| |
45 |
45 |
18 |
0 |
40 |
![]()
Q9 :
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data.
|
Income per day |
Number of persons |
|
0-100 |
4 |
|
100-200 |
8 |
|
200-300 |
9 |
|
300-400 |
10 |
|
400-500 |
7 |
|
500-600 |
5 |
|
600-700 |
4 |
|
700-800 |
3 |
Answer :
The following table is formed.
|
Income per day |
Number of persons fi |
Mid-point xi |
fi xi |
|
|
|
0 β 100 |
4 |
50 |
200 |
308 |
1232 |
|
100 β 200 |
8 |
150 |
1200 |
208 |
1664 |
|
200 β 300 |
9 |
250 |
2250 |
108 |
972 |
|
300 β 400 |
10 |
350 |
3500 |
8 |
80 |
|
400 β 500 |
7 |
450 |
3150 |
92 |
644 |
|
500 β 600 |
5 |
550 |
2750 |
192 |
960 |
|
600 β 700 |
4 |
650 |
2600 |
292 |
1168 |
|
700 β 800 |
3 |
750 |
2250 |
392 |
1176 |
|
|
50 |
|
17900 |
|
7896 |
Here,
![]()
Q10 :
Find the mean deviation about the mean for the data
|
Height in cms |
Number of boys |
|
95-105 |
9 |
|
105-115 |
13 |
|
115-125 |
26 |
|
125-135 |
30 |
|
135-145 |
12 |
Answer :
The following table is formed.
|
Height in cms |
Number of boys fi |
Mid-point xi |
fi xi |
|
|
|
95-105 |
9 |
100 |
900 |
25.3 |
227.7 |
|
105-115 |
13 |
110 |
1430 |
15.3 |
198.9 |
|
115-125 |
26 |
120 |
3120 |
5.3 |
137.8 |
|
125-135 |
30 |
130 |
3900 |
4.7 |
141 |
|
135-145 |
12 |
140 |
1680 |
14.7 |
176.4 |
|
145-155 |
10 |
150 |
1500 |
24.7 |
247 |
Here,
![]()
Q11 :
Calculate the mean deviation about median age for the age distribution of 100 persons given below:
|
Age |
Number |
|
16-20 |
5 |
|
21-25 |
6 |
|
26-30 |
12 |
|
31-35 |
14 |
|
36-40 |
26 |
|
41-45 |
12 |
|
46-50 |
16 |
|
51-55 |
9 |
Answer :
The given data is not continuous. Therefore, it has to be converted into continuous frequency distribution by subtracting 0.5 from the lower limit and adding 0.5 to the upper limit of each class interval.
The table is formed as follows.
|
Age |
Number fi |
Cumulative frequency (c.f.) |
Mid-point xi |
|xi β Med.| |
fi|xi β Med.| |
|
15.5-20.5 |
5 |
5 |
18 |
20 |
100 |
|
20.5-25.5 |
6 |
11 |
23 |
15 |
90 |
|
25.5-30.5 |
12 |
23 |
28 |
10 |
120 |
|
30.5-35.5 |
14 |
37 |
33 |
5 |
70 |
|
35.5-40.5 |
26 |
63 |
38 |
0 |
0 |
|
40.5-45.5 |
12 |
75 |
43 |
5 |
60 |
|
45.5-50.5 |
16 |
91 |
48 |
10 |
160 |
|
50.5-55.5 |
9 |
100 |
53 |
15 |
135 |
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
735 |
The class interval containing the ![]() or 50th item is 35.5 β 40.5.
Therefore, 35.5 β 40.5 is the median class.
or 50th item is 35.5 β 40.5.
Therefore, 35.5 β 40.5 is the median class.
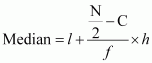 |
It is known that,
Here, l = 35.5, C = 37, f = 26, h = 5, and N = 100
![]()
![]()
Thus, mean deviation about the median is given by,
![]()
Exercise 15.2 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 371
Q1 :
Find the mean and variance for the data 6, 7, 10, 12, 13, 4, 8, 12
Answer :
6, 7, 10, 12, 13, 4, 8, 12
Mean, 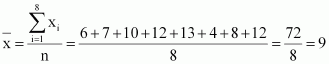 The following table is obtained.
The following table is obtained.
|
xi |
|
|
|
6 |
β3 |
9 |
|
7 |
β2 |
4 |
|
10 |
β1 |
1 |
|
12 |
3 |
9 |
|
13 |
4 |
16 |
|
4 |
β5 |
25 |
|
8 |
β1 |
1 |
|
12 |
3 |
9 |
|
|
|
74 |
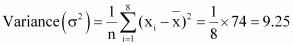 Q2 :
Q2 :
Find the mean and variance for the first n natural numbers
Answer :
The mean of first n natural numbers is calculated as follows.
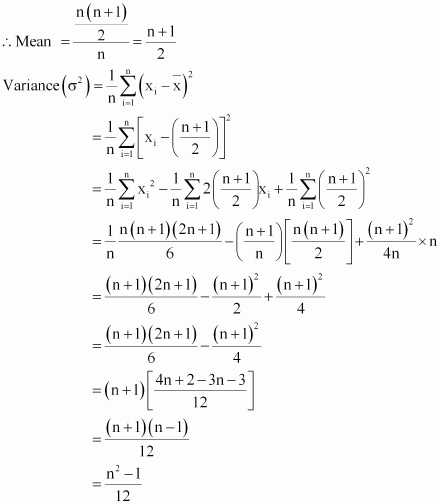
Q3 :
Find the mean and variance for the first 10 multiples of 3
Answer :
The first 10 multiples of 3 are
3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30
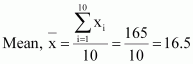 |
Here, number of observations, n = 10
The following table is obtained.
|
xi |
|
|
|
3 |
β13.5 |
182.25 |
|
6 |
β10.5 |
110.25 |
|
9 |
β7.5 |
56.25 |
|
12 |
β4.5 |
20.25 |
|
15 |
β1.5 |
2.25 |
|
18 |
1.5 |
2.25 |
|
21 |
4.5 |
20.25 |
|
24 |
7.5 |
56.25 |
|
27 |
10.5 |
110.25 |
|
30 |
13.5 |
182.25 |
|
|
|
742.5 |
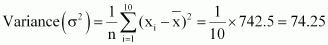 Q4 :
Q4 :
Find the mean and variance for the data
|
xi |
6 |
10 |
14 |
18 |
24 |
28 |
30 |
|
f i |
2 |
4 |
7 |
12 |
8 |
4 |
3 |
Answer :
The data is obtained in tabular form as follows.
|
xi |
f i |
fixi |
|
|
|
|
6 |
2 |
12 |
β13 |
169 |
338 |
|
10 |
4 |
40 |
β9 |
81 |
324 |
|
14 |
7 |
98 |
β5 |
25 |
175 |
|
18 |
12 |
216 |
β1 |
1 |
12 |
|
24 |
8 |
192 |
5 |
25 |
200 |
|
28 |
4 |
112 |
9 |
81 |
324 |
|
30 |
3 |
90 |
11 |
121 |
363 |
|
|
40 |
760 |
|
|
1736 |
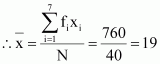 |
![]()
Q5 :
Find the mean and variance for the data
|
xi |
92 |
93 |
97 |
98 |
102 |
104 |
109 |
|
f i |
3 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
6 |
3 |
3 |
Answer :
The data is obtained in tabular form as follows.
|
xi |
f i |
fixi |
|
|
|
|
92 |
3 |
276 |
β8 |
64 |
192 |
|
93 |
2 |
186 |
β7 |
49 |
98 |
|
97 |
3 |
291 |
β3 |
9 |
27 |
|
98 |
2 |
196 |
β2 |
4 |
8 |
|
102 |
6 |
612 |
2 |
4 |
24 |
|
104 |
3 |
312 |
4 |
16 |
48 |
|
109 |
3 |
327 |
9 |
81 |
243 |
|
|
22 |
2200 |
|
|
640 |
![]()
Q6 :
Find the mean and standard deviation using short-cut method.
|
xi |
60 |
61 |
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 |
|
fi |
2 |
1 |
12 |
29 |
25 |
12 |
10 |
4 |
5 |
Answer :
The data is obtained in tabular form as follows.
|
xi |
fi |
|
yi2 |
fiyi |
fiyi2 |
|
60 |
2 |
β4 |
16 |
β8 |
32 |
|
61 |
1 |
β3 |
9 |
β3 |
9 |
|
62 |
12 |
β2 |
4 |
β24 |
48 |
|
63 |
29 |
β1 |
1 |
β29 |
29 |
|
64 |
25 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
65 |
12 |
1 |
1 |
12 |
12 |
|
66 |
10 |
2 |
4 |
20 |
40 |
|
67 |
4 |
3 |
9 |
12 |
36 |
|
68 |
5 |
4 |
16 |
20 |
80 |
|
|
100 |
220 |
|
0 |
286 |
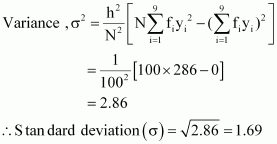 |
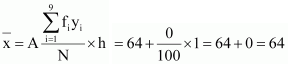 Mean,
Mean,
![]()
Q7 :
Find the mean and variance for the following frequency distribution.
|
Classes |
0-30 |
30-60 |
60-90 |
90-120 |
120-150 |
150-180 |
180-210 |
|
Frequencies |
2 |
3 |
5 |
10 |
3 |
5 |
2 |
Answer :
|
Class |
Frequency fi |
Mid-point xi |
|
yi2 |
fiyi |
fiyi2 |
|
0-30 |
2 |
15 |
β3 |
9 |
β6 |
18 |
|
30-60 |
3 |
45 |
β2 |
4 |
β6 |
12 |
|
60-90 |
5 |
75 |
β1 |
1 |
β5 |
5 |
|
90-120 |
10 |
105 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
120-150 |
3 |
135 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
3 |
|
150-180 |
5 |
165 |
2 |
4 |
10 |
20 |
|
180-210 |
2 |
195 |
3 |
9 |
6 |
18 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
|
2 |
76 |
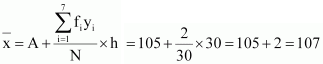 Mean,
Mean,
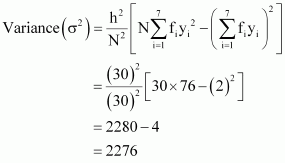
Q8 :
Find the mean and variance for the following frequency distribution.
|
Classes |
0-10 |
10-20 |
20-30 |
30-40 |
40-50 |
|
Frequencies |
5 |
8 |
15 |
16 |
6 |
Answer :
|
Class |
Frequency fi |
Mid-point xi |
|
yi2 |
fiyi |
fiyi2 |
|
0-10 |
5 |
5 |
β2 |
4 |
β10 |
20 |
|
10-20 |
8 |
15 |
β1 |
1 |
β8 |
8 |
|
20-30 |
15 |
25 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
30-40 |
16 |
35 |
1 |
1 |
16 |
16 |
|
40-50 |
6 |
45 |
2 |
4 |
12 |
24 |
|
|
50 |
|
|
|
10 |
68 |
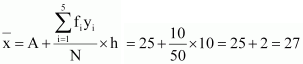 Mean,
Mean,
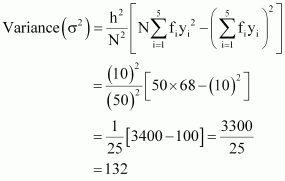
Q9 :
Find the mean, variance and standard deviation using short-cut method
|
Height in cms |
No. of children |
|
70-75 |
3 |
|
75-80 |
4 |
|
80-85 |
7 |
|
85-90 |
7 |
|
90-95 |
15 |
|
95-100 |
9 |
|
100-105 |
6 |
|
105-110 |
6 |
|
110-115 |
3 |
Answer :
|
Class Interval |
Frequency fi |
Mid-point xi |
|
yi2 |
fiyi |
fiyi2 |
|
70-75 |
3 |
72.5 |
β4 |
16 |
β12 |
48 |
|
75-80 |
4 |
77.5 |
β3 |
9 |
β12 |
36 |
|
80-85 |
7 |
82.5 |
β2 |
4 |
β14 |
28 |
|
85-90 |
7 |
87.5 |
β1 |
1 |
β7 |
7 |
|
90-95 |
15 |
92.5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
95-100 |
9 |
97.5 |
1 |
1 |
9 |
9 |
|
100-105 |
6 |
102.5 |
2 |
4 |
12 |
24 |
|
105-110 |
6 |
107.5 |
3 |
9 |
18 |
54 |
|
110-115 |
3 |
112.5 |
4 |
16 |
12 |
48 |
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
6 |
254 |
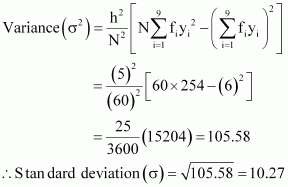 |
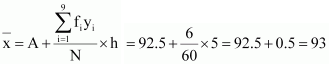 Mean,
Mean,
![]()
Q10 :
The diameters of circles (in mm) drawn in a design are given below:
|
Diameters |
No. of children |
|
33-36 |
15 |
|
37-40 |
17 |
|
41-44 |
21 |
|
45-48 |
22 |
|
49-52 |
25 |
Answer :
|
Class Interval |
Frequency fi |
Mid-point xi |
|
fi2 |
fiyi |
fiyi2 |
|
32.5-36.5 |
15 |
34.5 |
β2 |
4 |
β30 |
60 |
|
36.5-40.5 |
17 |
38.5 |
β1 |
1 |
β17 |
17 |
|
40.5-44.5 |
21 |
42.5 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
44.5-48.5 |
22 |
46.5 |
1 |
1 |
22 |
22 |
|
48.5-52.5 |
25 |
50.5 |
2 |
4 |
50 |
100 |
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
25 |
199 |
Here, N = 100, h = 4
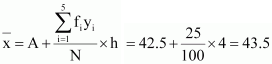 Let the assumed
mean, A, be 42.5.
Let the assumed
mean, A, be 42.5.
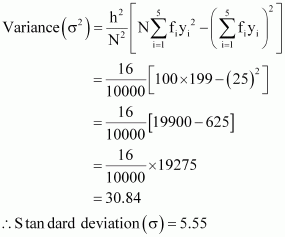 |
Mean,
![]()
Exercise 15.3 : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 375
Q1 :
From the data given below state which group is more variable, A or B?
|
Marks |
10-20 |
20-30 |
30-40 |
40-50 |
50-60 |
60-70 |
70-80 |
|
Group A |
9 |
17 |
32 |
33 |
40 |
10 |
9 |
|
Group B |
10 |
20 |
30 |
25 |
43 |
15 |
7 |
Answer :
Firstly, the standard deviation of group A is calculated as follows.
|
Marks |
Group A fi |
Mid-point xi |
|
yi2 |
fiyi |
fiyi2 |
|
10-20 |
9 |
15 |
β3 |
9 |
β27 |
81 |
|
20-30 |
17 |
25 |
β2 |
4 |
β34 |
68 |
|
30-40 |
32 |
35 |
β1 |
1 |
β32 |
32 |
|
40-50 |
33 |
45 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
50-60 |
40 |
55 |
1 |
1 |
40 |
40 |
|
60-70 |
10 |
65 |
2 |
4 |
20 |
40 |
|
70-80 |
9 |
75 |
3 |
9 |
27 |
81 |
|
|
150 |
|
|
|
β6 |
342 |
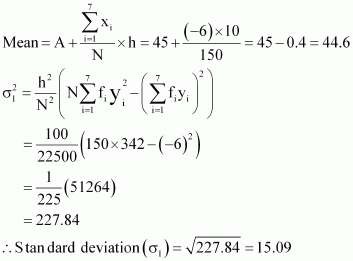 |
Here, h = 10, N = 150, A = 45
The standard deviation of group B is calculated as follows.
|
Marks |
Group B fi |
Mid-point xi |
|
yi2 |
fiyi |
fiyi2 |
|
10-20 |
10 |
15 |
β3 |
9 |
β30 |
90 |
|
20-30 |
20 |
25 |
β2 |
4 |
β40 |
80 |
|
30-40 |
30 |
35 |
β1 |
1 |
β30 |
30 |
|
40-50 |
25 |
45 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
50-60 |
43 |
55 |
1 |
1 |
43 |
43 |
|
60-70 |
15 |
65 |
2 |
4 |
30 |
60 |
|
70-80 |
7 |
75 |
3 |
9 |
21 |
63 |
|
|
150 |
|
|
|
β6 |
366 |
![]()
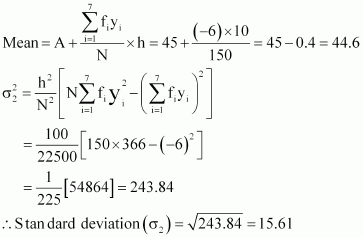 Since the mean of both the groups is same, the group with greater
standard deviation will be more variable. Thus,
group B has more variability in the marks.
Since the mean of both the groups is same, the group with greater
standard deviation will be more variable. Thus,
group B has more variability in the marks.
Q2 :
From the data given below state which group is more variable, A or B?
|
Marks |
10-20 |
20-30 |
30-40 |
40-50 |
50-60 |
60-70 |
70-80 |
|
Group A |
9 |
17 |
32 |
33 |
40 |
10 |
9 |
|
Group B |
10 |
20 |
30 |
25 |
43 |
15 |
7 |
Answer :
Firstly, the standard deviation of group A is calculated as follows.
|
Marks |
Group A fi |
Mid-point xi |
|
yi2 |
fiyi |
fiyi2 |
|
10-20 |
9 |
15 |
β3 |
9 |
β27 |
81 |
|
20-30 |
17 |
25 |
β2 |
4 |
β34 |
68 |
|
30-40 |
32 |
35 |
β1 |
1 |
β32 |
32 |
|
40-50 |
33 |
45 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
50-60 |
40 |
55 |
1 |
1 |
40 |
40 |
|
60-70 |
10 |
65 |
2 |
4 |
20 |
40 |
|
70-80 |
9 |
75 |
3 |
9 |
27 |
81 |
|
Ξ£ |
150 |
|
|
|
β6 |
342 |
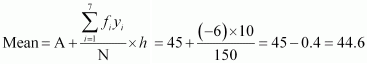 |
Here, h = 10, N = 150, A = 45
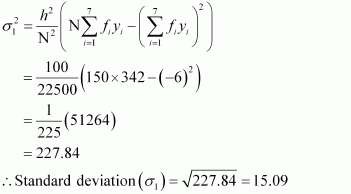
The standard deviation of group B is calculated as follows.
|
Marks |
Group B fi |
Mid-point xi |
|
yi2 |
fiyi |
fiyi2 |
|
10-20 |
10 |
15 |
β3 |
9 |
β30 |
90 |
|
20-30 |
20 |
25 |
β2 |
4 |
β40 |
80 |
|
30-40 |
30 |
35 |
β1 |
1 |
β30 |
30 |
|
40-50 |
25 |
45 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
50-60 |
43 |
55 |
1 |
1 |
43 |
43 |
|
60-70 |
15 |
65 |
2 |
4 |
30 |
60 |
|
70-80 |
7 |
75 |
3 |
9 |
21 |
63 |
|
Ξ£ |
150 |
|
|
|
β6 |
366 |

![]() Since
the mean of both the groups is same, the group with greater standard deviation
will be more variable. Thus, group B has more variability in the marks.
Since
the mean of both the groups is same, the group with greater standard deviation
will be more variable. Thus, group B has more variability in the marks.
Q3 :
From the prices of shares X and Y below, find out which is more stable in value:
|
X |
35 |
54 |
52 |
53 |
56 |
58 |
52 |
50 |
51 |
49 |
|
Y |
108 |
107 |
105 |
105 |
106 |
107 |
104 |
103 |
104 |
101 |
Answer :
The prices of the shares X are
35, 54, 52, 53, 56, 58, 52, 50, 51, 49
Here, the number of observations, N = 10
The following table is obtained corresponding to shares X.
|
xi |
|
|
|
35 |
β16 |
256 |
|
54 |
3 |
9 |
|
52 |
1 |
1 |
|
53 |
2 |
4 |
|
56 |
5 |
25 |
|
58 |
7 |
49 |
|
52 |
1 |
1 |
|
50 |
β1 |
1 |
|
51 |
0 |
0 |
|
49 |
β2 |
4 |
|
|
|
350 |
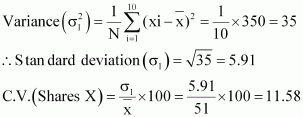 The prices of share Y are
The prices of share Y are
108, 107, 105, 105, 106, 107, 104, 103, 104, 101
The following table is obtained corresponding to shares Y.
|
yi |
|
|
|
108 |
3 |
9 |
|
107 |
2 |
4 |
|
105 |
0 |
0 |
|
105 |
0 |
0 |
|
106 |
1 |
1 |
|
107 |
2 |
4 |
|
104 |
β1 |
1 |
|
103 |
β2 |
4 |
|
104 |
β1 |
1 |
|
101 |
β4 |
16 |
|
|
|
40 |
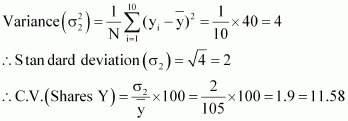
![]() C.V. of prices
of shares X is greater than the
C.V. of prices of shares Y. Thus, the prices
of shares Y are more stable
than the prices of shares X.
C.V. of prices
of shares X is greater than the
C.V. of prices of shares Y. Thus, the prices
of shares Y are more stable
than the prices of shares X.
Q4 :
An analysis of monthly wages paid to workers in two firms A and B, belonging to the same industry, gives the following results:
|
|
Firm A |
Firm B |
|
No. of wage earners |
586 |
648 |
|
Mean of monthly wages |
Rs 5253 |
Rs 5253 |
|
Variance of the distribution of wages |
100 |
121 |
(i) Which firm A or B pays larger amount as monthly wages?
(ii) Which firm, A or B, shows greater variability in individual wages?
Answer :
(i) Monthly wages of firm A = Rs 5253 Number of wage earners in firm A = 586
∴Total amount paid = Rs 5253 x 586
Monthly wages of firm B = Rs 5253 Number of wage earners in firm B = 648
∴Total amount paid = Rs 5253 x 648
![]() Thus, firm B pays the larger
amount as monthly wages as the number of wage earners in firm B are more than the number
of wage earners in firm A.
Thus, firm B pays the larger
amount as monthly wages as the number of wage earners in firm B are more than the number
of wage earners in firm A.
(ii) Variance of the distribution of wages in firm A = 100
![]()
![]() ∴ Standard
deviation of the distribution of wages in firm A ((Ο1) =
∴ Standard
deviation of the distribution of wages in firm A ((Ο1) =
Variance of the distribution of wages in firm = 121
![]() ∴ Standard deviation of
the distribution of wages in firm
∴ Standard deviation of
the distribution of wages in firm
The mean of monthly wages of both the firms is same i.e., 5253. Therefore, the firm with greater standard deviation will have more variability.
Thus, firm B has greater variability in the individual wages.
Q5 :
The following is the record of goals scored by team A in a football session:
|
No. of goals scored |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
No. of matches |
1 |
9 |
7 |
5 |
3 |
For the team B, mean number of goals scored per match was 2 with a standard deviation 1.25 goals. Find which team may be considered more consistent?
Answer :
The mean and the standard deviation of goals scored by team A are calculated as follows.
|
No. of goals scored |
No. of matches |
fixi |
xi2 |
fixi2 |
|
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
9 |
9 |
1 |
9 |
|
2 |
7 |
14 |
4 |
28 |
|
3 |
5 |
15 |
9 |
45 |
|
4 |
3 |
12 |
16 |
48 |
|
|
25 |
50 |
|
130 |
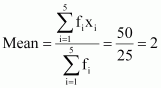
Thus, the mean of both the teams is same.
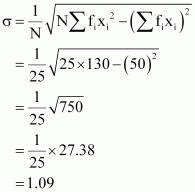
The standard deviation of team B is 1.25 goals.
The average number of goals scored by both the teams is same i.e., 2. Therefore, the team with lower standard deviation will be more consistent.
Thus, team A is more consistent than team B.
Q6 :
The sum and sum of squares corresponding to length x (in cm) and weight y
(in gm) of 50 plant products are given below:
Which is more varying, the length or weight?
Answer :
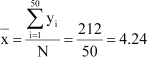 Here, N = 50
Here, N = 50
∴ Mean,
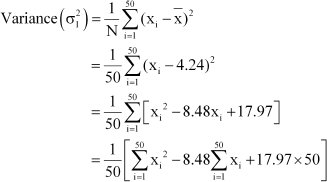
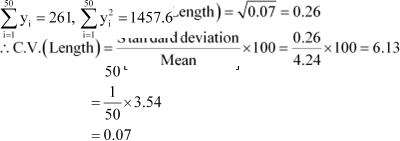 |
![]() Mean,
Mean,

Thus, C.V. of weights is greater than the C.V. of lengths. Therefore, weights vary more than the lengths.
Exercise Miscellaneous : Solutions of Questions on Page Number : 380
Q1 :
The mean and variance of eight observations are 9 and 9.25, respectively. If six of the observations are 6, 7, 10, 12, 12 and 13, find the remaining two observations.
Answer :
Let the remaining two observations be x and y. Therefore, the observations are 6, 7, 10, 12, 12, 13, x, y.
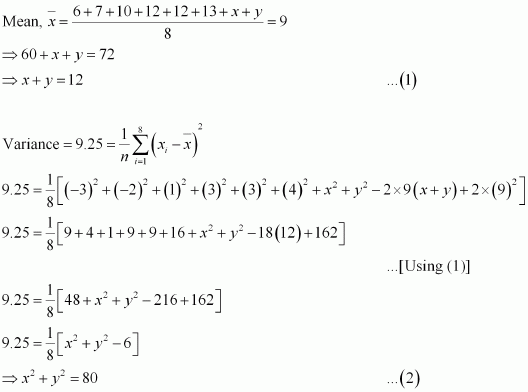
From (1), we obtain
x2 + y2 + 2xy = 144 β¦(3) From (2) and (3), we obtain
2xy = 64 β¦ (4)
Subtracting (4) from (2), we obtain
x2 + y2 β 2xy = 80 β 64 = 16
⇒ x β y = Β± 4 β¦ (5)
Therefore, from (1) and (5), we obtain
x = 8 and y = 4, when x β y = 4
x = 4 and y = 8, when x β y = β4
Thus, the remaining observations are 4 and 8.
Q2 :
The mean and variance of 7 observations are 8 and 16, respectively. If five of the observations are 2, 4, 10, 12 and 14. Find the remaining two observations.
Answer :
Let the remaining two observations be x and y.
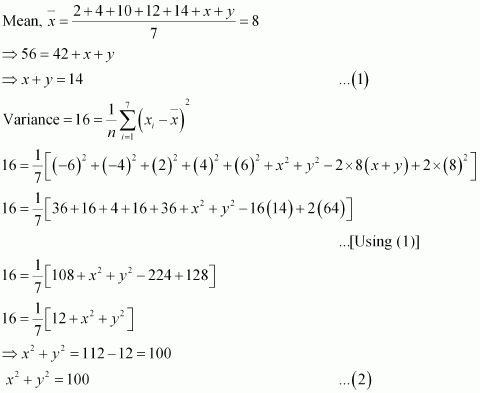 |
The observations are 2, 4, 10, 12, 14, x, y.
From (1), we obtain
x2 + y2 + 2xy = 196 β¦ (3) From (2) and (3), we obtain
2xy = 196 β 100
⇒ 2xy = 96 β¦ (4)
Subtracting (4) from (2), we obtain
x2 + y2 β 2xy = 100 β 96
⇒ (x β y)2 = 4
⇒ x β y = Β± 2 β¦ (5)
Therefore, from (1) and (5), we obtain
x = 8 and y = 6 when x β y = 2
x = 6 and y = 8 when x β y = β 2
Thus, the remaining observations are 6 and 8.
Q3 :
The mean and standard deviation of six observations are 8 and 4, respectively. If each observation is multiplied by 3, find the new mean and new standard deviation of the resulting observations.
Answer :
Let the observations be x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, and x6.
It is given that mean is 8 and standard deviation is 4.
If each observation is multiplied by 3 and the resulting observations are yi, then
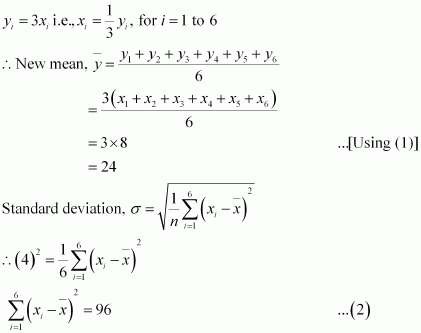
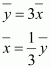 |
From (1) and (2), it can be observed that,
Substituting the values
of xi and ![]() in
(2), we obtain
in
(2), we obtain
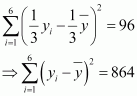
Therefore, variance of new observations =
Q4 :
Given that ![]() is the mean and Ο2
is the variance
of n observations x1, x2 β¦ xn.
Prove that the mean and variance of the observations ax1,
ax2,
ax3 β¦axn are
is the mean and Ο2
is the variance
of n observations x1, x2 β¦ xn.
Prove that the mean and variance of the observations ax1,
ax2,
ax3 β¦axn are ![]() and a2
Ο2,
respectively (a ≠ 0).
and a2
Ο2,
respectively (a ≠ 0).
Answer :
The given n observations are x1, x2 β¦ xn. Mean = ![]()
Variance = Ο2
If each observation is multiplied by a and the new observations are yi, then
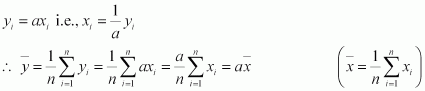
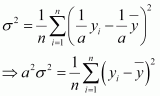 |
Therefore, mean of the observations, ax1, ax2 β¦ axn, is
Thus, the variance of the observations, ax1, ax2 β¦ axn, is a2 Ο2.
![]()
Q5 :
The mean and standard deviation of 20 observations are found to be 10 and 2, respectively. On rechecking, it was found that an observation 8 was incorrect. Calculate the correct mean and standard deviation in each of the following cases:
(i) If wrong item is omitted.
(ii) If it is replaced by 12.
Answer :
(i) Number of observations (n) = 20 Incorrect mean = 10
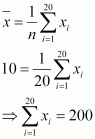 |
Incorrect standard deviation = 2
That is, incorrect sum of observations = 200 Correct sum of observations = 200 β 8 = 192
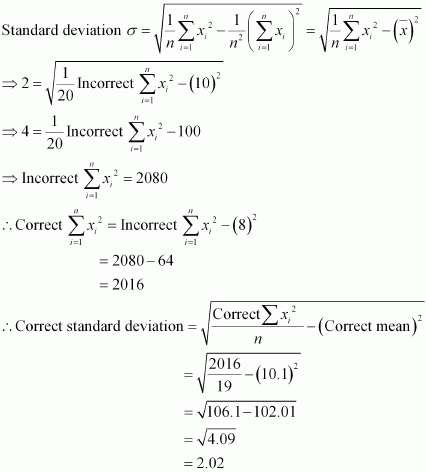 |
∴ Correct mean
(ii) When 8 is replaced by 12, Incorrect sum of observations = 200
∴ Correct sum of observations = 200 β 8 + 12 = 204
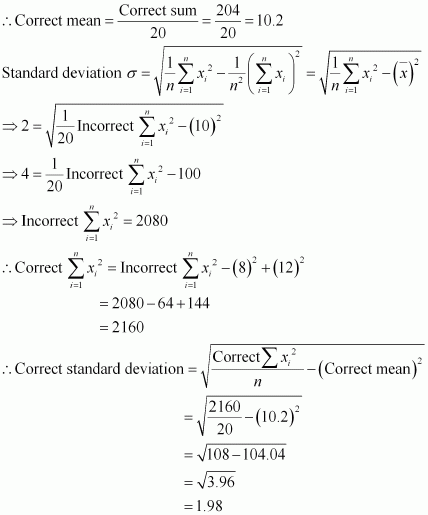
Q6 :
The mean and standard deviation of marks obtained by 50 students of a class in three subjects, Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry are given below:
|
Subject |
Mathematics |
Physics |
Chemistry |
|
Mean |
42 |
32 |
40.9 |
|
Standard deviation |
12 |
15 |
20 |
Which of the three subjects shows the highest variability in marks and which shows the lowest?
Answer :
Standard deviation of Mathematics = 12 Standard deviation of Physics = 15
![]() Standard deviation of Chemistry = 20
Standard deviation of Chemistry = 20
The coefficient of variation (C.V.) is given by .
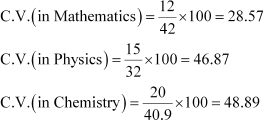 |
The subject with greater C.V. is more variable than others.
Therefore, the highest variability in marks is in Chemistry and the lowest variability in marks is in Mathematics.
Q7 :
The mean and standard deviation of a group of 100 observations were found to be 20 and 3, respectively. Later on it was found that three observations were incorrect, which were recorded as 21, 21 and 18. Find the mean and standard deviation if the incorrect observations are omitted.
Answer :
Number of observations (n) = 100
Incorrect mean ![]()
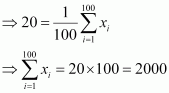 |
Incorrect standard deviation
∴ Incorrect sum of observations = 2000
⇒ Correct sum of observations = 2000 β 21 β 21 β 18 = 2000 β 60 = 1940