Integrals
NCERT Textbook Solution (Laptop/Desktop is best to view this page)
Class XII Chapter 7 – Integrals Maths
![]()
Exercise 7.1
Question 1: sin 2x Answer
The anti derivative of sin 2x is a function of x whose derivative is sin 2x.It is known that,
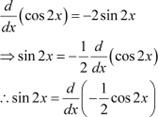 |
![]() Therefore, the anti derivative of
Therefore, the anti derivative of
Question 2:
Cos 3x Answer
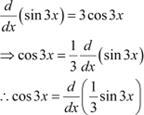 |
The anti derivative of cos 3x is a function of x whose derivative is cos 3x. It is known that,
![]() Therefore, the anti derivative of .
Therefore, the anti derivative of .
Question 3:
e2x
Answer
The anti derivative of e2x is the function of x whose derivative is e2x. It is known that,
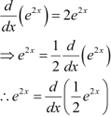
![]() Therefore, the anti derivative of .
Therefore, the anti derivative of .
Question 4:
Answer
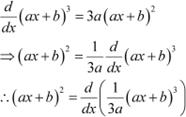 |
![]() Therefore, the anti derivative of .
Therefore, the anti derivative of .
Question 5:
Answer
![]()
![]() The anti derivative of is the function of x whose
derivative is
The anti derivative of is the function of x whose
derivative is
.
It is known that,
![]()
![]()
![]() Therefore, the anti derivative of is .
Therefore, the anti derivative of is .
Question 6:
Answer
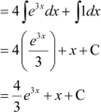 |
Question 7:
Answer
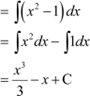 |
Question 8:
Answer
![]()
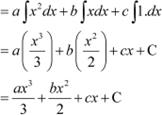 |
Question 9:
Answer
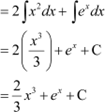 |
Question 10:
Answer
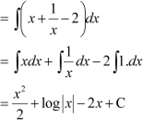 |
Question 11:
Answer
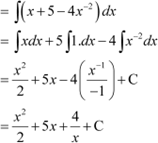 |
Question 12:
Answer
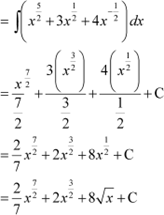 |
Question 13:
Answer
On dividing, we obtain
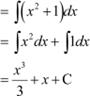 |
Question 14:
Answer
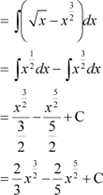 |
Question 15:
Answer
![]()
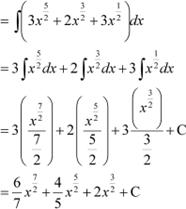 |
Question 16:
Answer
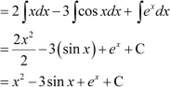 |
Question 17:
Answer
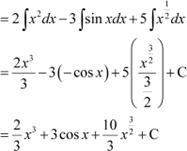
Question 18:
Answer
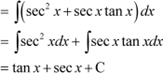 |
Question 19:
Answer
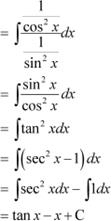
Question 20:
Answer
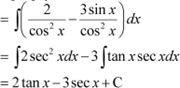 |
![]() Question 21:
Question 21:
![]()
![]() The anti derivative of equals
The anti derivative of equals
![]()
![]() (A) (B)
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
Answer
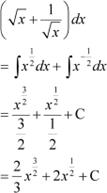
Hence, the correct Answer is C.
![]() Question 22:
Question 22:
![]()
![]() If such that f(2) = 0, then f(x) is
If such that f(2) = 0, then f(x) is
![]()
![]() (A) (B)
(A) (B)
(C) (D)
Answer
It is given that,
![]() ∴Anti derivative of
∴Anti derivative of
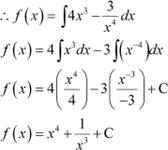 ∴
∴
Also,
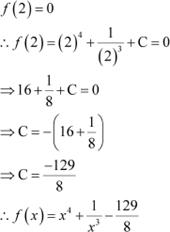 |
Hence, the correct Answer is A.
Exercise 7.2
Question 1:
Answer
![]() Let = t
Let = t
∴2x dx = dt
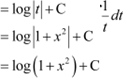 |
Question 2:
Answer
![]() Let
log |x| = t
Let
log |x| = t
∴
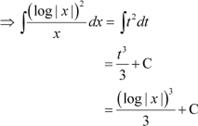
Question 3:
Answer
Let 1 + log x = t
![]() ∴
∴
Question 4:
sin x ⋅ sin (cos x)
Answer
sin x ⋅ sin (cos x)
Let cos x = t
∴ −sin x dx = dt
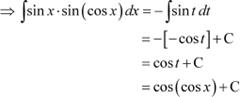 |
Question 5:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
∴ 2adx = dt
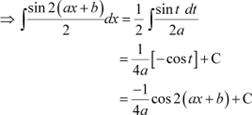
Question 6:
Answer
Let ax + b = t
⇒ adx = dt
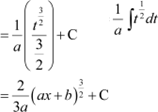 |
![]() Question 7:
Question 7:
Answer Let
∴ dx = dt
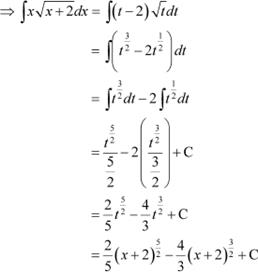 |
Question 8:
Answer
Let 1 + 2x2 = t
∴ 4xdx = dt
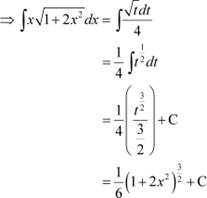
![]() Question 9:
Question 9:
Answer Let
∴ (2x + 1)dx = dt
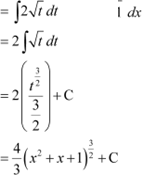 |
Question 10:
Answer
![]()
![]() Let
Let
∴
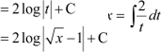 |
![]() Question 11:
Question 11:
Answer Let
∴ dx = dt
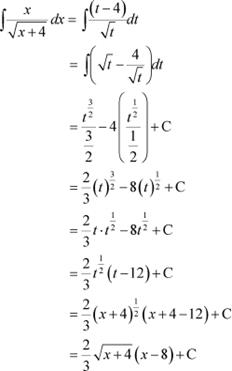
![]() Question 12:
Question 12:
Answer Let
![]() ∴
∴
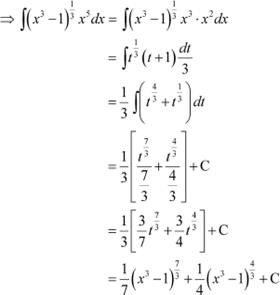
![]() Question 13:
Question 13:
Answer Let
∴ 9x2 dx = dt
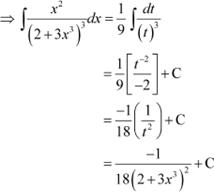
Question 14:
Answer
![]() Let log x
= t
Let log x
= t
∴
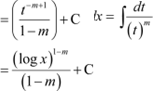 |
Question 15:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
∴ −8x dx = dt
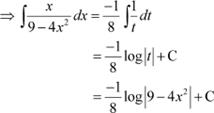 |
![]() Question 16:
Question 16:
Answer Let
∴ 2dx = dt
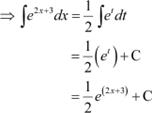 |
![]() Question 17:
Question 17:
Answer Let
∴ 2xdx = dt
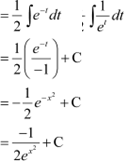 |
Question 18:
Answer Let
![]()
![]() ∴
∴
![]()
Question 19:
Answer
Dividing numerator and denominator by ex, we obtain
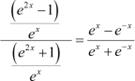 |
![]() Let
Let
![]() ∴
∴
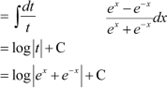 |
Question 20:
Answer Let
![]()
![]() ∴
∴
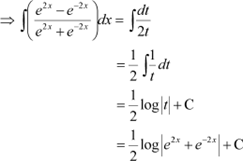 |
Question 21:
Answer
![]()
Let 2x − 3 = t
∴ 2dx = dt
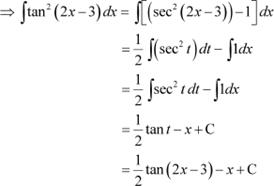
Question 22:
Answer
Let 7 − 4x = t
∴ −4dx = dt
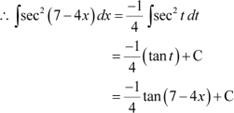 |
![]() Question 23:
Question 23:
Answer Let
![]() ∴
∴
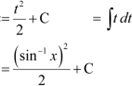 |
Question 24:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
![]() ∴
∴
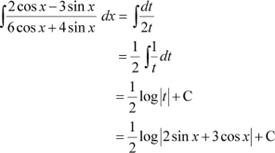 |
Question 25:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
![]() ∴
∴
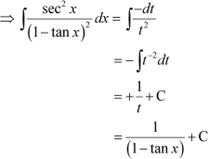 |
Question 26:
Answer Let
![]()
![]() ∴
∴
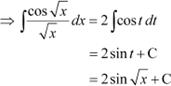
Question 27:
Answer
Let sin 2x = t
![]() ∴
∴
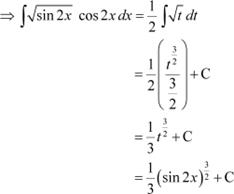 |
![]() Question 28:
Question 28:
Answer Let
∴ cos x dx = dt
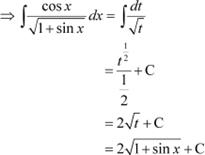 |
Question 29: cot x log sin x Answer
Let log sin x = t
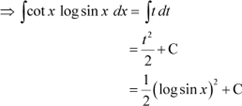 |
Question 30:
Answer
Let 1 + cos x = t
∴ −sin x dx = dt
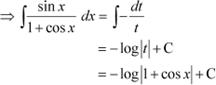 |
Question 31:
Answer
Let 1 + cos x = t
∴ −sin x dx = dt
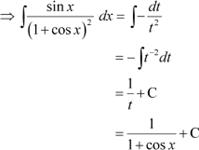 |
Question 32:
Answer
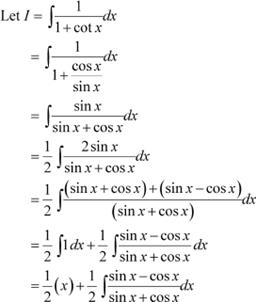
Let sin x + cos x = t ⇒ (cos x − sin x) dx = dt
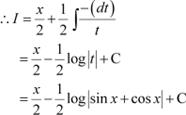 |
Question 33:
Answer
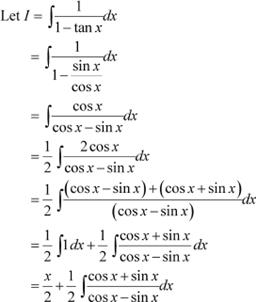
Put cos x − sin x = t ⇒ (−sin x − cos x) dx = dt
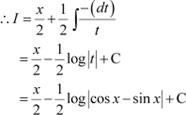 |
Question 34:
Answer
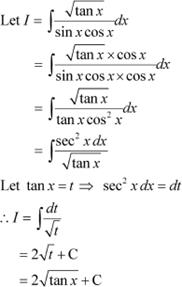
Question 35:
Answer
![]() Let 1 + log x = t
Let 1 + log x = t
∴
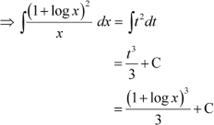 |
Question 36:
Answer
![]()
![]() Let
Let
∴
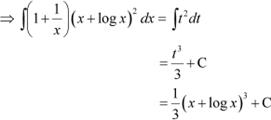 |
Question 37:
Answer Let x4 = t
∴ 4x3 dx = dt
![]()
![]() Let
Let
![]() ∴
∴
From (1), we obtain
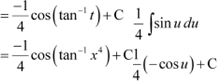 |
![]() Question 38:
Question 38:
equals
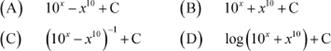 |
Answer Let
![]()
![]() ∴
∴
![]()
Hence, the correct Answer is D.
Question 39:
![]() equals
equals
![]() A.
A.
![]() B.
B.
![]() C.
C.
![]() D.
D.
Answer
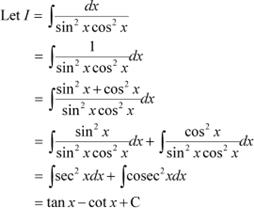 |
Hence, the correct Answer is B.
Exercise 7.3
Question 1:
Answer
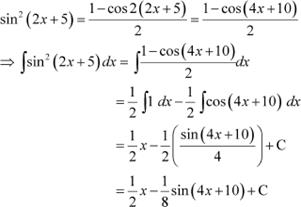 |
Question 2:
Answer
![]() It is known that,
It is known that,
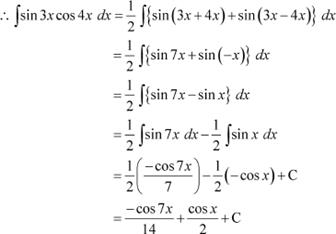 |
Question 3:
![]() cos 2x cos
4x cos 6x
Answer
cos 2x cos
4x cos 6x
Answer
It is known that,
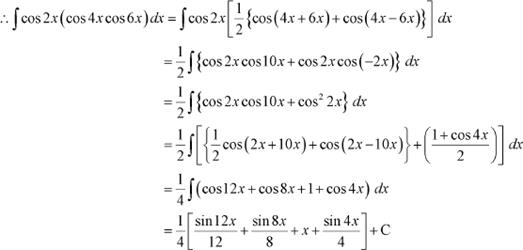 |
![]() Question 4: sin3 (2x + 1) Answer
Question 4: sin3 (2x + 1) Answer
Let
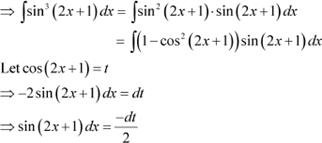 |
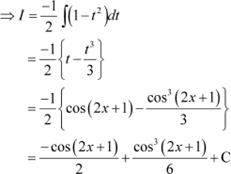
Question 5: sin3 x cos3 x Answer
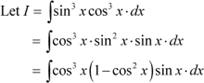
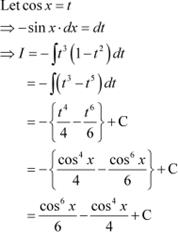 |
Question 6:
sin x sin 2x sin 3x Answer
![]() It is known that,
It is known that,
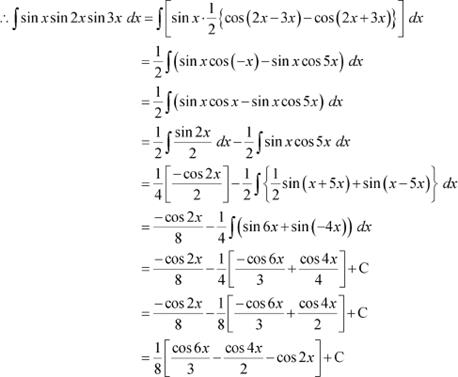 |
![]() Question 7: sin
4x sin 8x Answer
Question 7: sin
4x sin 8x Answer
It is known that,
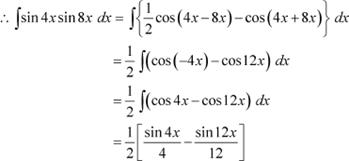
Question 8:
Answer
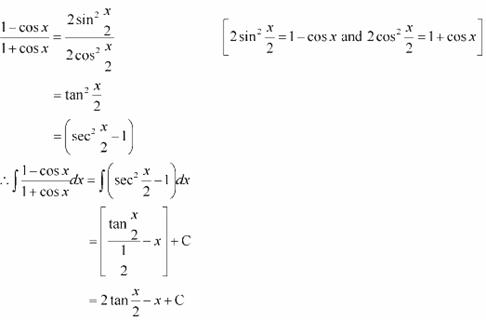
Question 9:
Answer
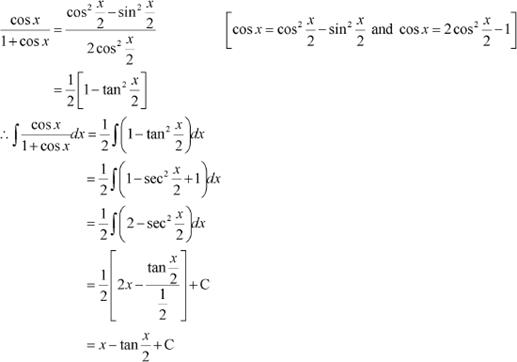
Question 10:
sin4 x
Answer
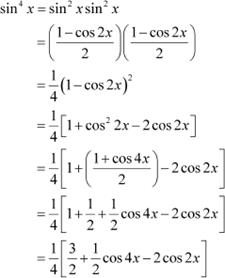
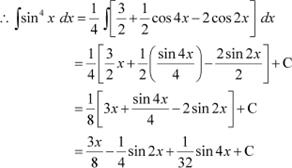 |
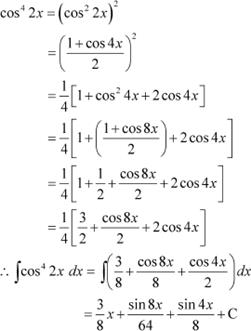
Question 11: cos4 2x Answer
Question 12:
Answer
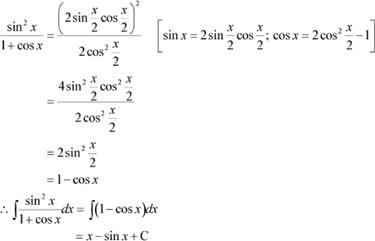 |
Question 13:
Answer
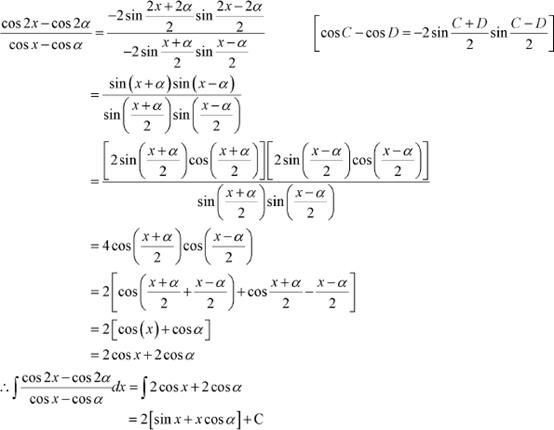 |
Question 14:
Answer

Question 15:
Answer
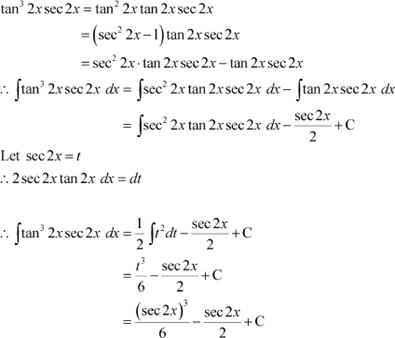
Question 16:
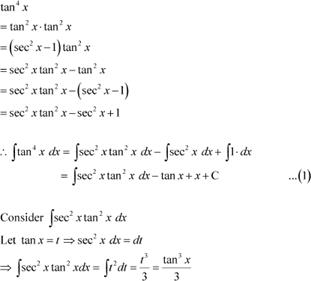 |
tan4x Answer
From equation (1), we obtain
Question 17:
Answer
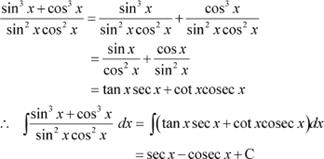 |
Question 18:
Answer
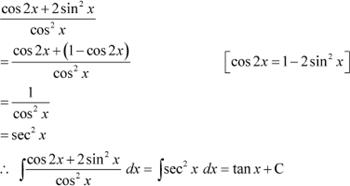 |
Question 19:
![]()
Answer
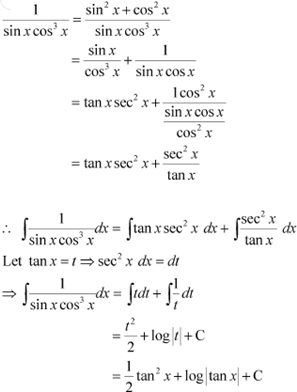 |
Question 20:
Answer
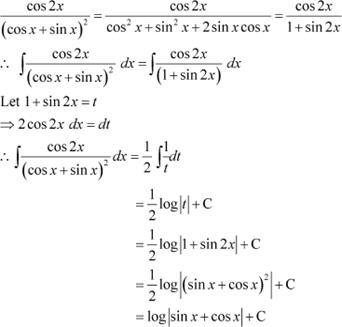
Question 21: sin−1 (cos x) Answer
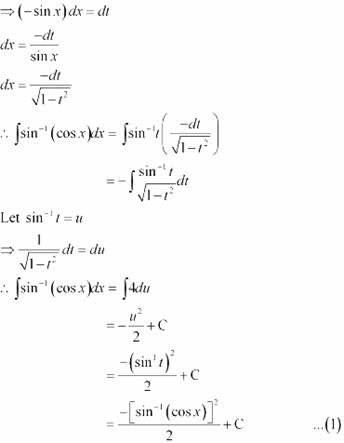
It is known that,
Substituting in equation (1), we obtain
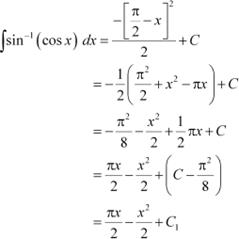
Question 22:
Answer
![]() Question 23:
Question 23:
is equal to
A. tan x + cot x + C
B. tan x + cosec x + C
C. − tan x + cot x + C
D.
tan x + sec x + C Answer
Hence, the correct Answer is A.
![]() Question 24:
Question 24:
equals
A. − cot (exx) + C
B. tan (xex) + C
C. tan (ex) + C
D.
cot (ex) + C Answer
Let exx = t
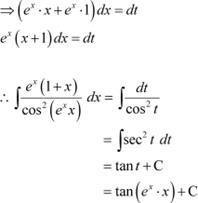
Hence, the correct Answer is B.
Exercise 7.4
Question 1:
Answer Let x3 = t
∴ 3x2 dx = dt
Question 2:
Answer Let 2x = t
∴ 2dx = dt
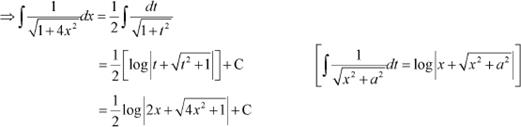
Question 3:
Answer
Let 2 − x = t
⇒ −dx = dt
Question 4:
Answer Let 5x = t
∴ 5dx = dt
Question 5:
Answer
Question 6:
Answer Let x3 = t
∴ 3x2 dx = dt
Question 7:
Answer
From (1), we obtain
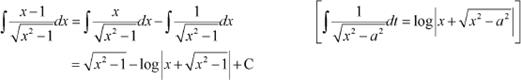
Question 8:
Answer Let x3 = t
⇒ 3x2 dx = dt
Question 9:
Answer
Let tan x = t
∴ sec2x dx = dt
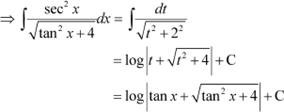
Question 10:
Answer
Question 11:
Answer
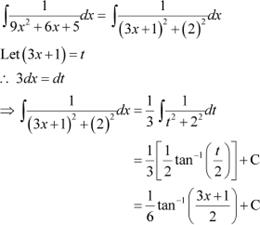
Question 12:
Answer
Question 13:
Answer
Question 14:
Answer
Question 15:
Answer

Question 16:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term on both sides, we obtain
4A = 4 ⇒ A = 1
A + B = 1 ⇒ B = 0
Let 2x2 + x − 3 = t
∴ (4x + 1) dx = dt
Question 17:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term on both sides, we obtain
From (1), we obtain
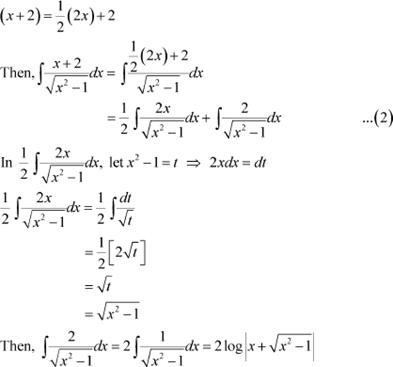
From equation (2), we obtain
Question 18:
Answer
Equating the coefficient of x and constant term on both sides, we obtain
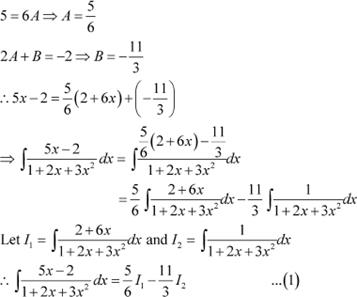
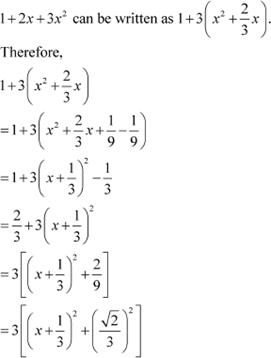
Substituting equations (2) and (3) in equation (1), we obtain
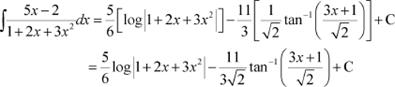
Question 19:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term, we obtain
2A = 6 ⇒ A = 3
−9A + B = 7 ⇒ B = 34
∴ 6x + 7 = 3 (2x − 9) + 34


Substituting equations (2) and (3) in (1), we obtain
Question 20:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term on both sides, we obtain
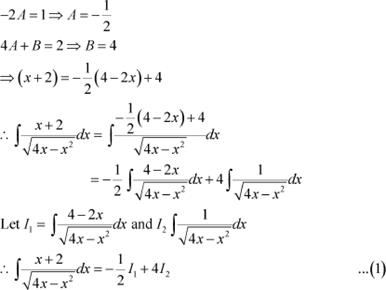
Using equations (2) and (3) in (1), we obtain
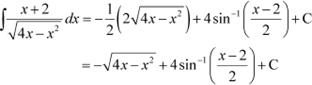
Question 21:
Answer
Let x2 + 2x +3 = t
⇒ (2x + 2) dx =dt
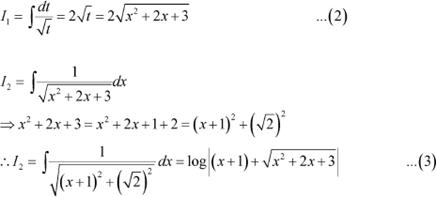
Using equations (2) and (3) in (1), we obtain
Question 22:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term on both sides, we obtain
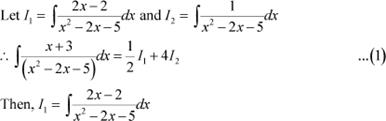
Substituting (2) and (3) in (1), we obtain
Question 23:
Answer
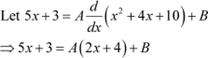
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term, we obtain
Using equations (2) and (3) in (1), we obtain
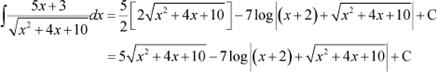
![]() Question 24:
Question 24:
equals
A. x tan−1 (x + 1) + C
B. tan− 1 (x + 1) + C
C. (x + 1) tan−1 x + C
D.
tan−1 x + C Answer
Hence, the correct Answer is B.
![]() Question 25:
Question 25:
![]() equals
equals
![]() A.
A.
![]() B.
B.
C.
![]() D.
D.
Answer
Hence, the correct Answer is B.
Exercise 7.5
Question 1:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term, we obtain
A + B = 1 2A + B = 0
On solving, we obtain
A = −1 and B = 2
Question 2:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term, we obtain
A + B = 0
−3A + 3B = 1
On solving, we obtain
Question 3:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Substituting x = 1, 2, and 3 respectively in equation (1), we obtain
A = 1, B = −5, and C = 4
Question 4:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Substituting x = 1, 2, and 3 respectively in equation (1), we obtain
Question 5:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Substituting x = −1 and −2 in equation (1), we obtain
A = −2 and B = 4
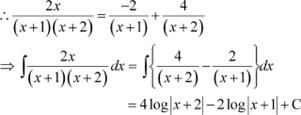
Question 6:
Answer
It can be seen that the given integrand is not a proper fraction. Therefore, on dividing (1 − x2) by x(1 − 2x), we obtain
![]() Let
Let
![]() Substituting x = 0 and in equation
(1), we obtain
Substituting x = 0 and in equation
(1), we obtain
A = 2 and B = 3
Substituting in equation (1), we obtain
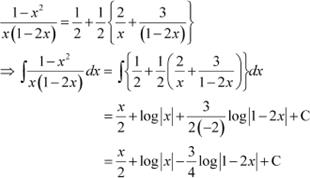
Question 7:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Equating the coefficients of x2, x, and constant term, we obtain
A + C = 0
−A + B = 1
−B + C = 0
On solving these equations, we obtain
From equation (1), we obtain
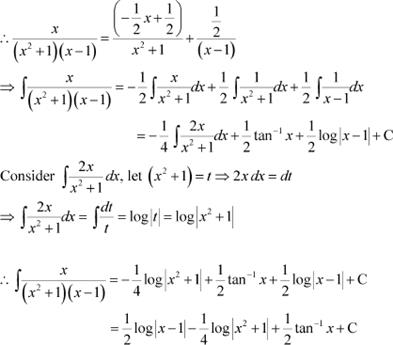
Question 8:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Substituting x = 1, we obtain
Equating the coefficients of x2 and constant term, we obtain
A + C = 0
−2A + 2B + C = 0
On solving, we obtain
![]()
Question 9:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Substituting x = 1 in equation (1), we obtain
B = 4
Equating the coefficients of x2 and x, we obtain
A + C = 0
B − 2C = 3
On solving, we obtain
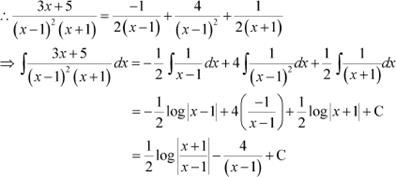
Question 10:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Equating the coefficients of x2 and x, we obtain
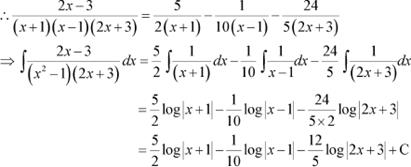
Question 11:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Substituting x = −1, −2, and 2 respectively in equation (1), we obtain
Question 12:
Answer
It can be seen that the given integrand is not a proper fraction. Therefore, on dividing (x3 + x + 1) by x2 − 1, we obtain
![]() Let
Let
Substituting x = 1 and −1 in equation (1), we obtain
Question 13:
Answer
Equating the coefficient of x2, x, and constant term, we obtain
A − B = 0 B − C = 0 A + C = 2
On solving these equations, we obtain
A = 1, B = 1, and C = 1
Question 14:
Answer
Equating the coefficient of x and constant term, we obtain
A = 3
2A + B = −1 ⇒ B = −7
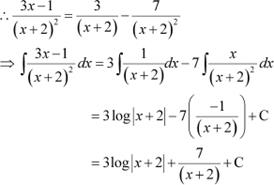
Question 15:
Answer
Equating the coefficient of x3, x2, x, and constant term, we obtain
On solving these equations, we obtain
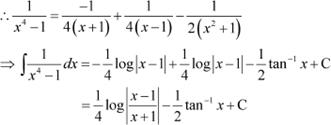
Question 16:
![]() [Hint: multiply
numerator and denominator by xn − 1 and put xn = t]
[Hint: multiply
numerator and denominator by xn − 1 and put xn = t]
Answer
Multiplying numerator and denominator by xn − 1, we obtain
Substituting t = 0, −1 in equation (1), we obtain
A = 1 and B = −1
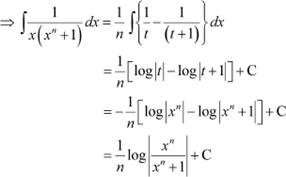
Question 17:
![]() [Hint: Put sin x = t]
[Hint: Put sin x = t]
Answer
Substituting t = 2 and then t = 1 in equation (1), we obtain
A = 1 and B = −1
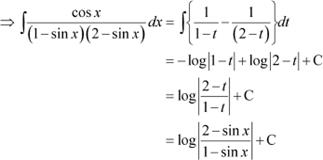
Question 18:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x3, x2, x, and constant term, we obtain
A + C = 0
B + D = 4 4A + 3C = 0
4B + 3D = 10
On solving these equations, we obtain
A = 0, B = −2, C = 0, and D = 6
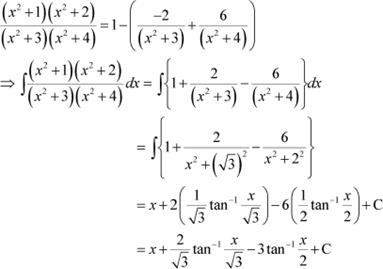
Question 19:
Answer
Let x2 = t ⇒ 2x dx = dt
Substituting t = −3 and t = −1 in equation (1), we obtain
![]()
Question 20:
Answer
Multiplying numerator and denominator by x3, we obtain
Let x4 = t ⇒ 4x3dx = dt
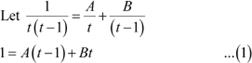
Substituting t = 0 and 1 in (1), we obtain
A = −1 and B = 1
Question 21:
![]() [Hint: Put ex = t]
[Hint: Put ex = t]
Answer
Let ex = t ⇒ ex dx = dt
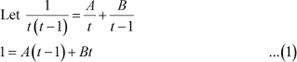
Substituting t = 1 and t = 0 in equation (1), we obtain
A = −1 and B = 1
Question 22:
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
![]() C.
C. ![]()
D.
Answer
Substituting x = 1 and 2 in (1), we obtain
A = −1 and B = 2
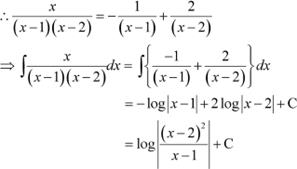
Hence, the correct Answer is B.
Question 23:
![]()
![]() A.
A.
![]() B.
B.
![]() C.
C.
D.
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x2, x, and constant term, we obtain
A + B = 0
C = 0
A = 1
On solving these equations, we obtain
A = 1, B = −1, and C = 0
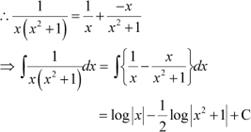
Hence, the correct Answer is A.
Exercise 7.6
Question 1:
x sin x
![]() Answer
Answer
Let I =
Taking x as first function and sin x as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
Question 2:
Answer
Let I = ![]()
Taking x as first function and sin 3x as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
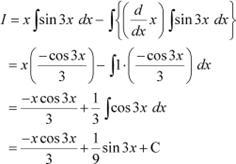
Question 3:
Answer
Let ![]()
Taking x2 as first function and ex as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
Again integrating by parts, we obtain
Question 4:
x logx Answer
Let ![]()
Taking log x as first function and x as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
Question 5:
x log 2x Answer
Let ![]()
Taking log 2x as first function and x as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
Question 6:
x2 log x
Answer
Let ![]()
Taking log x as first function and x2 as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
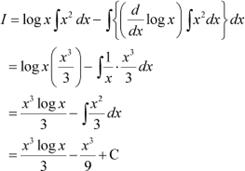
Question 7:
Answer
Let ![]()
![]() Question 8:
Question 8:
Answer Let
Question 9:
Answer
Let ![]()
Taking cos−1 x as first function and x as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
![]()
Page 106 of 216
Question 10:
Answer
![]() Let
Let ![]()
Taking as first function and 1 as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
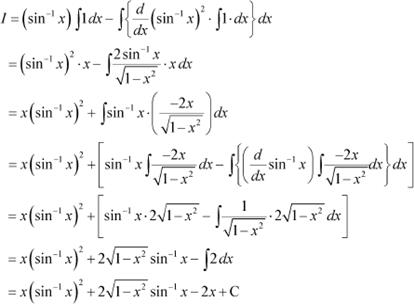
Question 11:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
![]()
![]()
![]() Taking as first function and as second
function and integrating by parts, we obtain
Taking as first function and as second
function and integrating by parts, we obtain
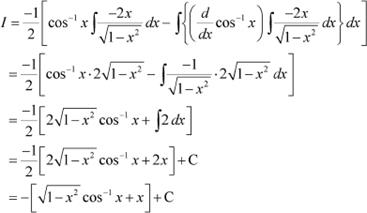
Question 12:
Answer
Let ![]()
Taking x as first function and sec2x as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
Question 13:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Question 14:
Answer
Again integrating by parts, we obtain
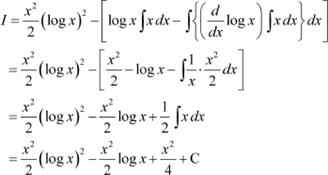
Question 15:
Answer
Let ![]() Let
I = I1 + I2 … (1)
Let
I = I1 + I2 … (1)
Where, ![]() and
and ![]()
Taking log x as first function and x2 as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
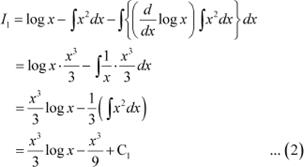
Taking log x as first function and 1 as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
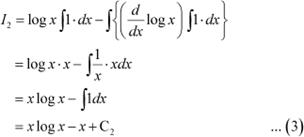
Using equations (2) and (3) in (1), we obtain
Question 16:
Answer Let
![]()
![]() Let
Let
![]()
![]() ⇒
⇒
![]() ⇒
⇒
It is known that,
Question 17:
![]() Answer
Answer
Let
![]()
![]() Let ⇒
Let ⇒
It is known that, ![]()
Question 18:
Answer
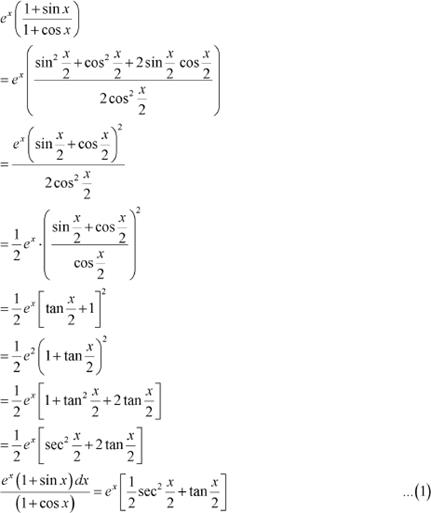
![]()
![]() Let ⇒
Let ⇒
![]() It is known that,
It is known that,
From equation (1), we obtain
Question 19:
![]()
Answer
![]()
![]() Also, let ⇒
Also, let ⇒
It is known that, ![]()
Question 20:
Answer
![]()
![]()
![]() Let ⇒
Let ⇒
It is known that,
Question 21:
Answer
![]() Let
Let
Integrating by parts, we obtain
Again integrating by parts, we obtain
Question 22:
Answer
![]()
![]() Let ⇒
Let ⇒
![]() = 2θ
= 2θ
![]()
![]() ⇒
⇒
Integrating by parts, we obtain
Question 23:
![]() equals
equals
Answer
![]()
![]() Let
Let ![]() Also, let ⇒
Also, let ⇒
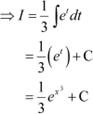
Hence, the correct Answer is A.
Question 24:
![]() equals
equals
Answer
Let ![]() Also, let ⇒
Also, let ⇒
![]()
![]()
![]() It is known that,
It is known that, ![]() Hence, the correct Answer is B.
Hence, the correct Answer is B.
Exercise 7.7
Question 1:
Answer
Question 2:
Answer
Question 3:
Answer
Question 4:
Answer
Question 5:
![]()
Answer
Question 6:
Answer
Question 7:
Answer
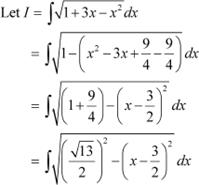
Question 8:
Answer
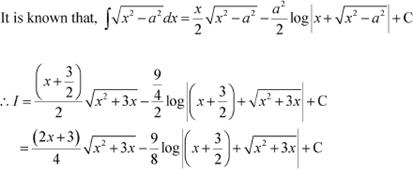
Question 9:
Answer
Question 10:
![]()
![]() is equal to
is equal to
![]() A.
A.
![]() B.
B.
C.
![]() D.
D.
Answer
Hence, the correct Answer is A.
Question 11:
![]()
![]() is equal to
is equal to
![]() A.
A.
![]() B.
B.
![]() C.
C.
D.
Answer
Hence, the correct Answer is D.
Exercise 7.8
Question 1:
Answer
It is known that,
Question 2:
Answer
It is known that,
Question 3:
![]()
Answer
It is known that,
Question 4:
Answer
It is known that,
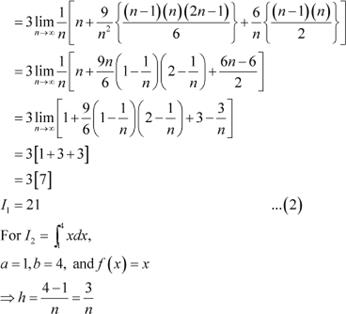
From equations (2) and (3), we obtain
![]()
Question 5:
Answer
It is known that,

Question 6:
Answer
It is known that,
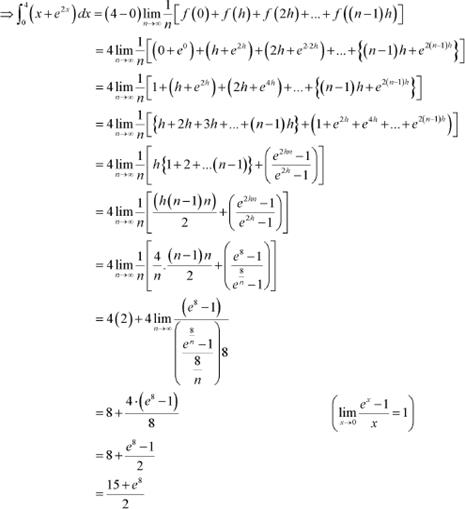
Exercise 7.9
Question 1:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 2:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 3:
![]()
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 4:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
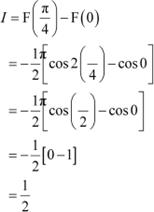
Question 5:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 6:
Answer
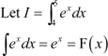
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 7:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 8:
Answer
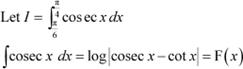
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 9:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 10:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 11:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 12:
![]()
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 13:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 14:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 15:
Answer
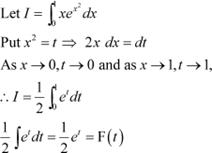
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 16:
Answer
Let ![]()
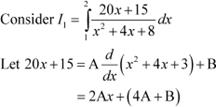
Equating the coefficients of x and constant term, we obtain A = 10 and B = −25
Substituting the value of I1 in (1), we obtain
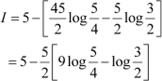
Question 17:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 18:
Answer
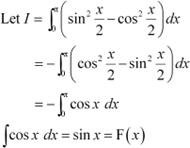
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Question 19:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
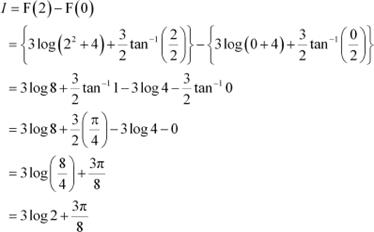
Question 20:
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
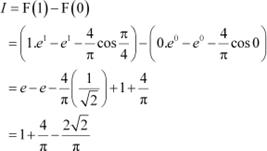
![]() Question 21:
Question 21:
![]() equals
equals
![]() A.
A.
![]() B.
B.
![]() C.
C.
D.
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
Hence, the correct Answer is D.
![]() Question 22:
Question 22:
![]() equals
equals
![]() A.
A.
![]() B.
B.
![]() C.
C.
D.
Answer
By second fundamental theorem of calculus, we obtain
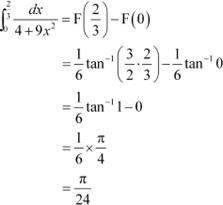
Hence, the correct Answer is C.
Exercise 7.10
Question 1:
Answer
When x = 0, t = 1 and when x = 1, t = 2
Question 2:
Answer
![]() Also, let
Also, let
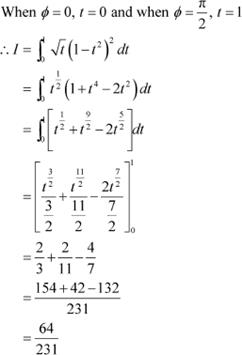
Question 3:
Answer
Also, let x = tanθ ⇒ dx = sec2θ dθ
![]() When x = 0, θ = 0 and when x = 1,
When x = 0, θ = 0 and when x = 1,
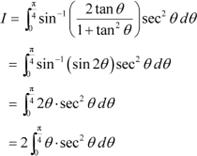
Takingθas first function and sec2θ as second function and integrating by parts, we obtain
Question 4:
Answer
Let x + 2 = t2 ⇒ dx = 2tdt
![]() When x = 0, and when x = 2,
t = 2
When x = 0, and when x = 2,
t = 2
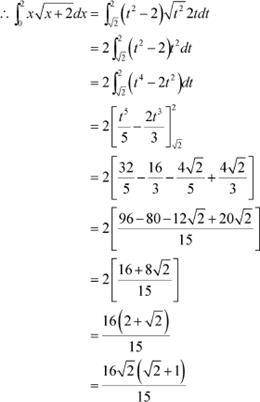
Question 5:
Answer
Let cos x = t ⇒ −sinx dx = dt
![]() When x = 0, t = 1 and when
When x = 0, t = 1 and when
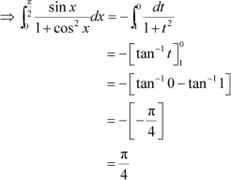
Question 6:
Answer
![]() Let ⇒ dx = dt
Let ⇒ dx = dt
![]()
Page 153 of 216
Question 7:
Answer
Let x + 1 = t ⇒ dx = dt
When x = −1, t = 0 and when x = 1, t = 2
Question 8:
Answer
Let 2x = t ⇒ 2dx = dt
When x = 1, t = 2 and when x = 2, t = 4
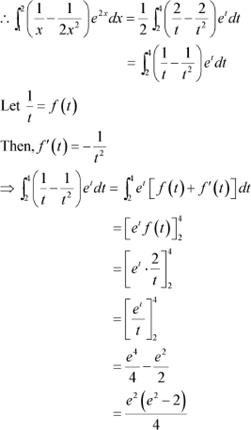
![]() Question 9:
Question 9:
The value of the integral is
A. 6
B. 0
C. 3
D. 4 Answer
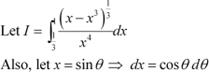
Let cotθ = t ⇒ −cosec2θ dθ= dt
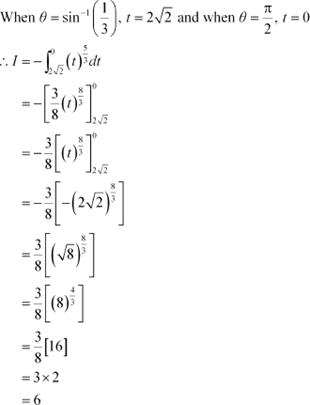
Hence, the correct Answer is A.
![]() Question 10:
Question 10:
If
A. cos x + x sin x
B. x sin x
C. x cos x
D. sin x + x cos x
Answer
Integrating by parts, we obtain
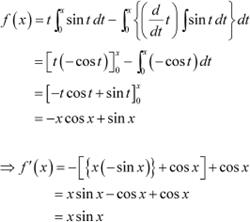
Hence, the correct Answer is B.
Exercise 7.11
Question 1:
Answer
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Question 2:
Answer
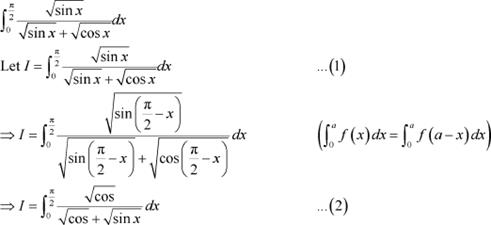
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Question 3:
Answer
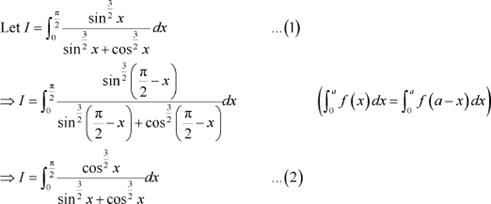
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Question 4:
Answer
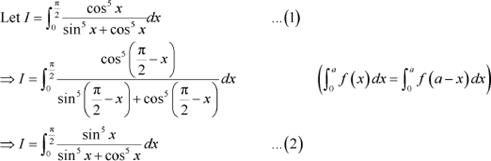
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Question 5:
Answer
It can be seen that (x + 2) ≤ 0 on [−5, −2] and (x + 2) ≥ 0 on [−2, 5].
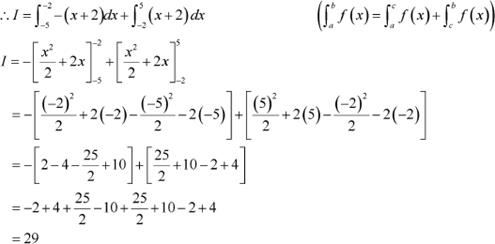
Question 6:
Answer
It can be seen that (x − 5) ≤ 0 on [2, 5] and (x − 5) ≥ 0 on [5, 8].
Question 7:
Answer
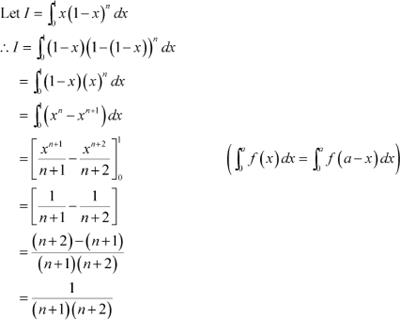
Question 8:
Answer
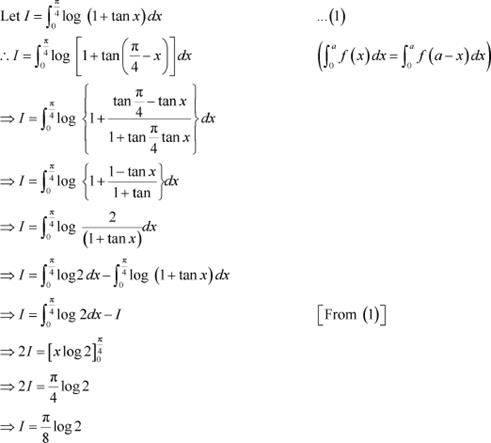
Question 9:
Answer
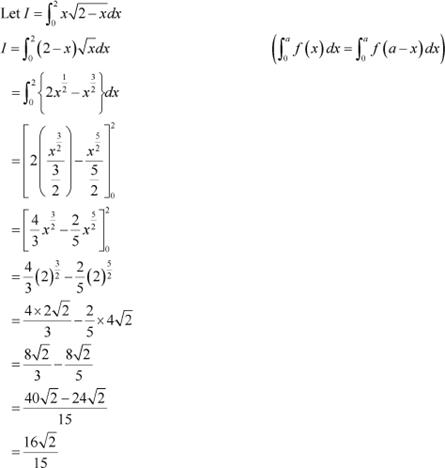
Question 10:
Answer
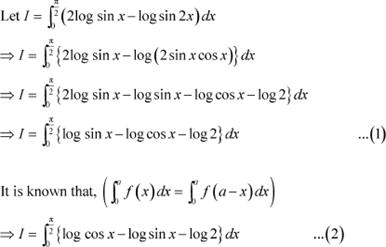
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Question 11:
Answer
As sin2 (−x) = (sin (−x))2 = (−sin x)2 = sin2x, therefore, sin2x is an even function.
![]() It is known that if f(x) is an even function, then
It is known that if f(x) is an even function, then
Question 12:
Answer
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
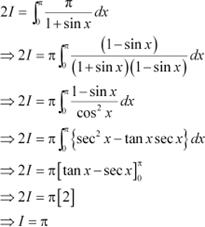
Question 13:
Answer
![]()
![]() As sin7 (−x) = (sin (−x))7 = (−sin x)7 = −sin7x, therefore, sin2x is an odd function. It is known that, if f(x) is an odd function, then
As sin7 (−x) = (sin (−x))7 = (−sin x)7 = −sin7x, therefore, sin2x is an odd function. It is known that, if f(x) is an odd function, then
Question 14:
Answer
It is known that,
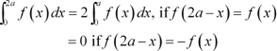
Question 15:
Answer
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Question 16:
Answer
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
sin (π − x) = sin x
Adding (4) and (5), we obtain
Let 2x = t ⇒ 2dx = dt
![]() When x = 0, t = 0 and when
When x = 0, t = 0 and when
Question 17:
Answer
![]() It is known that,
It is known that,
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Question 18:
Answer
It can be seen that, (x − 1) ≤ 0 when 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 and (x − 1) ≥ 0 when 1 ≤ x ≤ 4
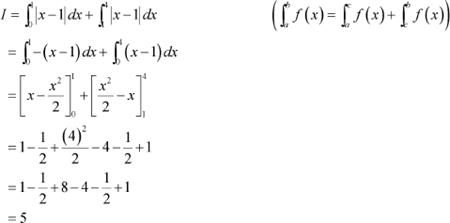
![]() Question 19:
Question 19:
![]() Show that if f and g are defined
as and
Show that if f and g are defined
as and
Answer
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Question 20:
![]() The value of is
The value of is
A. 0
B. 2
C. π
D.
It is known that if f(x) is an even function, then and if f(x) is an odd function, then
Hence, the correct Answer is C.
![]() Question 21:
Question 21:
The value of is
![]() A. 2
A. 2
B.
C. 0
D. ![]()
Answer
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Hence, the correct Answer is C.
Miscellaneous Solutions
Question 1:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x2, x, and constant term, we obtain
−A + B − C = 0
B + C = 0
A = 1
On solving these equations, we obtain
From equation (1), we obtain
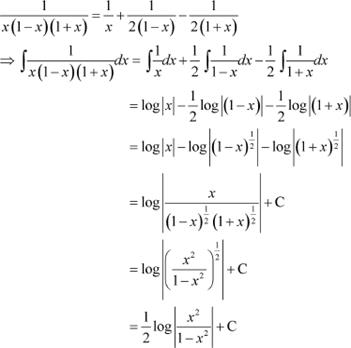
Question 2:
Answer
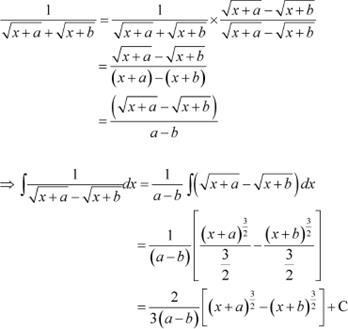
Question 3:
![]()
![]() [Hint: Put ]
[Hint: Put ]
Answer
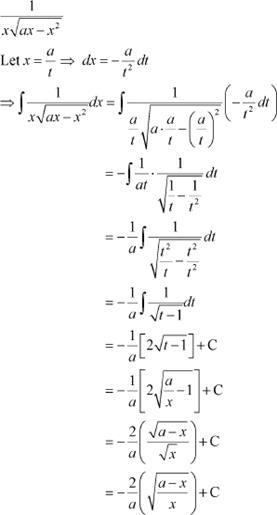
Question 4:
Answer
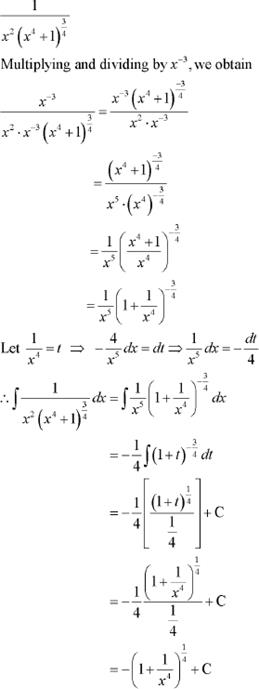
Question 5:
Answer
On dividing, we obtain
Question 6:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x2, x, and constant term, we obtain
A + B = 0 B + C = 5 9A + C = 0
On solving these equations, we obtain
From equation (1), we obtain
Question 7:
Answer
![]()
Let x − a = t ⇒ dx = dt
Question 8:
Answer
Question 9:
Answer
![]()
Let sin x = t ⇒ cos x dx = dt
Question 10:
Answer
Question 11:
Answer

Question 12:
Answer
Let x4 = t ⇒ 4x3 dx = dt
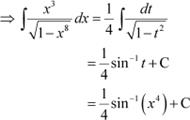
Question 13:
Answer
Let ex = t ⇒ ex dx = dt
Question 14:
Answer
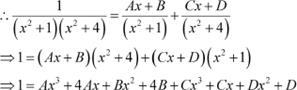
Equating the coefficients of x3, x2, x, and constant term, we obtain
A + C = 0 B + D = 0 4A + C = 0
4B + D = 1
On solving these equations, we obtain
From equation (1), we obtain
Question 15:
Answer
![]() = cos3 x × sin x
= cos3 x × sin x
Let cos x = t ⇒ −sin x dx = dt
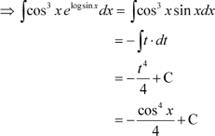
Question 16:
Answer
Question 17:
Answer
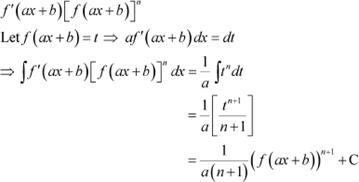
Question 18:
Answer
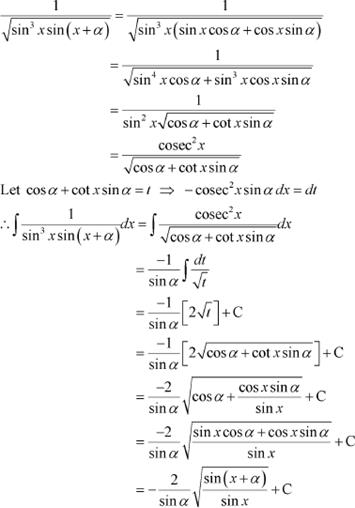
Question 19:
Answer
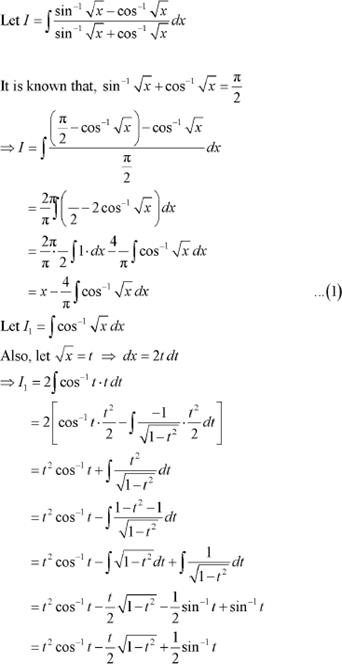
From equation (1), we obtain
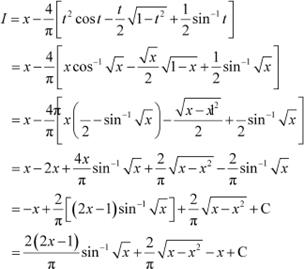
Question 20:
Answer
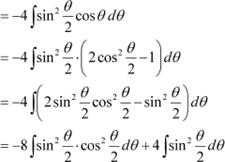
Question 21:
Answer
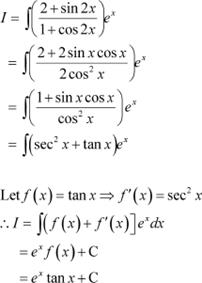
Question 22:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x2, x,and constant term, we obtain
A + C = 1
3A + B + 2C = 1
2A + 2B + C = 1
On solving these equations, we obtain
A = −2, B = 1, and C = 3
From equation (1), we obtain
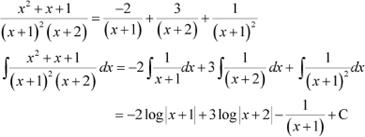
Question 23:
Answer
Question 24:
Answer
Integrating by parts, we obtain
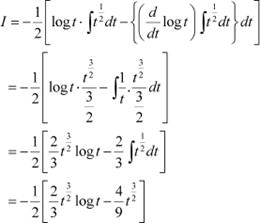
Question 25:
Answer
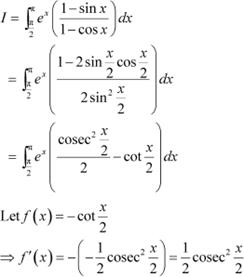
Question 26:
Answer
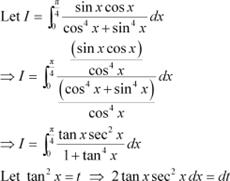
![]() When x = 0, t = 0 and
When x = 0, t = 0 and
Question 27:
Answer
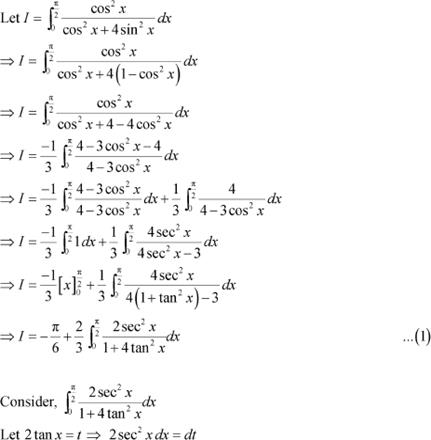
![]()
![]() When and when
When and when
Question 28:
Answer
![]()
![]() When and when
When and when
![]()
![]() As , therefore,
As , therefore, ![]() is an even function.
It is known that if f(x) is an even function, then
is an even function.
It is known that if f(x) is an even function, then
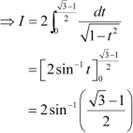
Question 29:
Answer
Question 30:
Answer
Question 31:
Answer
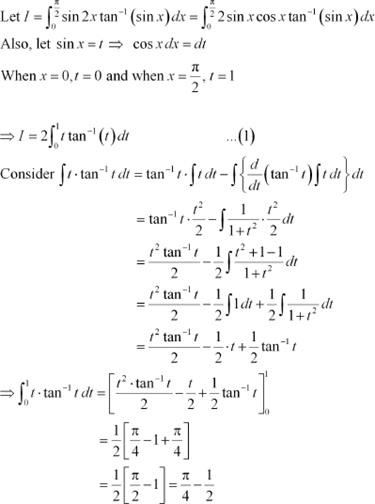
From equation (1), we obtain
Question 32:
Answer
![]()
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Question 33:
![]()
Answer
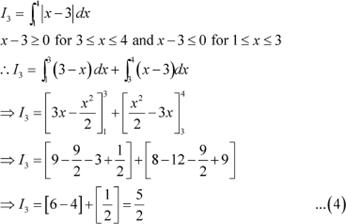
From equations (1), (2), (3), and (4), we obtain
Question 34:
Answer
Equating the coefficients of x2, x, and constant term, we obtain
A + C = 0 A + B = 0 B = 1
On solving these equations, we obtain
A = −1, C = 1, and B = 1
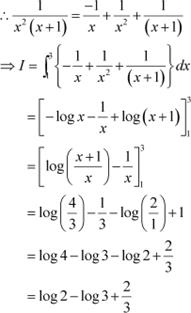
Hence, the given result is proved.
Question 35:
Answer
Integrating by parts, we obtain
Question 36:
Answer
Therefore, f (x) is an odd function.
![]() It is known that if f(x) is an odd function, then
It is known that if f(x) is an odd function, then
Hence, the given result is proved.
Question 37:
Answer
Question 38:
Answer
Hence, the given result is proved.
Question 39:
Answer
Integrating by parts, we obtain
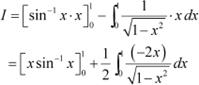
Let 1 − x2 = t ⇒ −2x dx = dt
Hence, the given result is proved.
![]() Question 40:
Question 40:
Evaluate as a limit of a sum. Answer
It is known that,
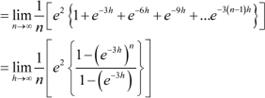
![]() Question 41:
Question 41:
![]() is equal to
is equal to
A.
![]()
![]() B.
B.
C.
![]() D.
D.
Answer
Hence, the correct Answer is A.
![]() Question 42:
Question 42:
![]() is equal to
is equal to
A.
![]() B.
B.
![]()
![]() C.
C.
D.
Answer
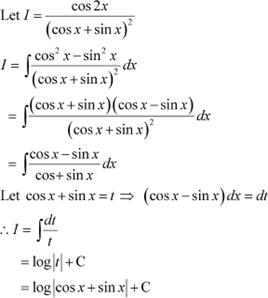
Hence, the correct Answer is B.
![]() Question 43:
Question 43:
![]()
![]() If then is equal to
If then is equal to
![]() A.
A.
![]() B.
B.
![]() C.
C.
D.
Answer
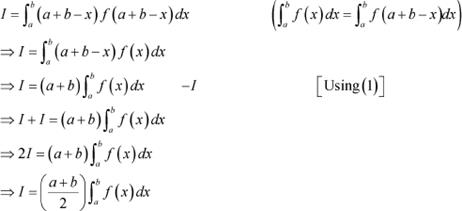
Hence, the correct Answer is D.
![]() Question 44:
Question 44:
The value of is
A. 1
B. 0
C. ![]() − 1
− 1
D.
Answer
Adding (1) and (2), we obtain
Hence, the correct Answer is B.