Vector algebra
NCERT Textbook Solution (Laptop/Desktop is best to view this page)
![]()
Exercise 10.1
Question 1:
Represent graphically a displacement of 40 km, 30° east of north. Answer
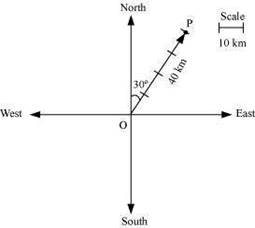
Here, vector ![]() represents the displacement of 40 km, 30° East of North.
represents the displacement of 40 km, 30° East of North.
Question 2:
Classify the following measures as scalars and vectors.
(i) 10 kg (ii) 2 metres north-west (iii) 40°
(iv) 40 watt (v) 10–19 coulomb (vi) 20 m/s2 Answer
(i) 10 kg is a scalar quantity because it involves only magnitude.
(ii) 2 meters north-west is a vector quantity as it involves both magnitude and direction.
(iii) 40° is a scalar quantity as it involves only magnitude.
(iv) 40 watts is a scalar quantity as it involves only magnitude.
(v) 10–19 coulomb is a scalar quantity as it involves only magnitude.
(vi) 20 m/s2 is a vector quantity as it involves magnitude as well as direction.
Question 3:
Classify the following as scalar and vector quantities.
(i) time period (ii) distance (iii) force
(iv) velocity (v) work done Answer
(i) Time period is a scalar quantity as it involves only magnitude.
(ii) Distance is a scalar quantity as it involves only magnitude.
(iii) Force is a vector quantity as it involves both magnitude and direction.
(iv) Velocity is a vector quantity as it involves both magnitude as well as direction.
(v) Work done is a scalar quantity as it involves only magnitude.
Question 4:
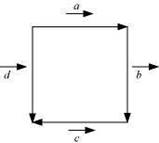 |
In Figure, identify the following vectors.
(i) Coinitial (ii) Equal (iii) Collinear but not equal Answer
(i)
![]() Vectors and
Vectors and ![]() are coinitial because
they have the same initial point.
are coinitial because
they have the same initial point.
(ii) Vectors ![]() and
and ![]() are equal because they have the same magnitude
and direction.
are equal because they have the same magnitude
and direction.
(iii) Vectors ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear but not equal. This is because
although they are parallel, their directions are not the same.
are collinear but not equal. This is because
although they are parallel, their directions are not the same.
Question 5:
Answer the following as true or false.
(i) ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
(ii) Two collinear vectors are always equal in magnitude.
(iii) Two vectors having same magnitude are collinear.
(iv) Two collinear vectors having the same magnitude are equal.
Answer
(i) True.
Vectors ![]() and
and ![]() are parallel to the same line.
are parallel to the same line.
(ii) False.
Collinear vectors are those vectors that are parallel to the same line.
(iii) False.
Exercise 10.2
Question 1:
Compute the magnitude of the following vectors:
Answer
The given vectors are:
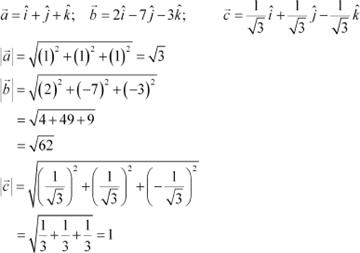 |
Question 2:
 |
Write two different vectors having same magnitude. Answer
Hence,
![]() are two different vectors having the same magnitude. The vectors are different because
they have different directions.
are two different vectors having the same magnitude. The vectors are different because
they have different directions.
Question 3:
Write two different vectors having same direction. Answer
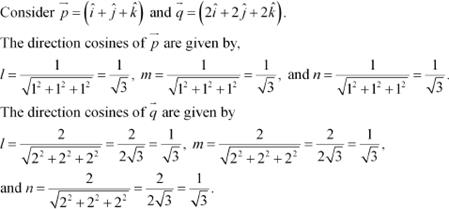
The direction
cosines of ![]() are the same. Hence, the two vectors have the same direction.
are the same. Hence, the two vectors have the same direction.
Question 4:
Find the values of x and y so that the vectors ![]() are
equal Answer
are
equal Answer
The two vectors ![]() will be equal if their corresponding components are equal.
will be equal if their corresponding components are equal.
Hence, the required values of x and y are 2 and 3 respectively.
Question 5:
Find the scalar and vector components of the vector with initial point (2, 1) and terminal point (–5, 7).
Answer
The vector with the initial point P (2, 1) and terminal point Q (–5, 7) can be given by,
Hence, the required scalar components are –7 and 6 while the vector components are
Question 6:
Find the sum of the vectors
![]() .
.
Answer
The given vectors are ![]() .
.
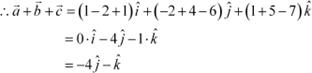 |
Question 7:
Find the unit vector
in the direction of the vector ![]() . Answer
. Answer
![]()
![]()
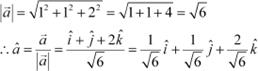 The unit vector in the direction of vector is given by
The unit vector in the direction of vector is given by ![]() .
.
Question 8:
Find the unit vector in the direction of vector ![]() , where P and Q are the points (1, 2, 3) and (4, 5, 6), respectively.
, where P and Q are the points (1, 2, 3) and (4, 5, 6), respectively.
Answer
The given points are P (1, 2, 3) and Q (4, 5, 6).
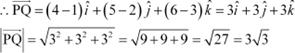 |
![]() Hence, the unit vector in the direction of
Hence, the unit vector in the direction of ![]() is
is
.
Question 9:
For given vectors, ![]() and
and ![]() ,
find the unit vector in the direction of the vector
,
find the unit vector in the direction of the vector
![]()
Answer
The given vectors are ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
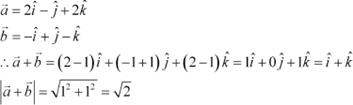 |
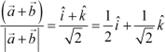 Hence, the unit vector in the direction of
Hence, the unit vector in the direction of ![]() is
is
.
Question 10:
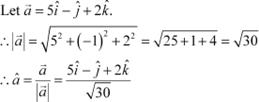 |
Find a vector in the direction of vector
Hence, the vector in the direction of vector
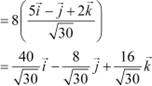
Question 11:
Show that the vectors
![]() are collinear. Answer
are collinear. Answer
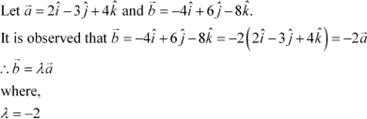 .
.
Hence, the given vectors are collinear.
Question 12:
Find the direction cosines of the vector
![]() Hence, the direction cosines
of
Hence, the direction cosines
of
Question 13:
Find the direction cosines of the vector joining the points A (1, 2, –3) and B (–1, –2, 1) directed from A to B.
Answer
The given points are A (1, 2, –3) and B (–1, –2, 1).
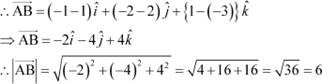
![]() Hence, the direction cosines
of
Hence, the direction cosines
of ![]() are
are
Question 14:
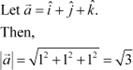 |
Show that the vector
Therefore, the direction cosines
of ![]()
Now, let α, β, and γbe the angles formed
by ![]() with the positive directions of x, y,
and z
with the positive directions of x, y,
and z
axes.
Then, we have ![]()
Hence, the given vector is equally inclined to axes OX, OY, and OZ.
Question 15:
Find the position vector of a point R which divides the line joining two points P and Q
whose position vectors are ![]() respectively, in the ration
2:1
respectively, in the ration
2:1
(i) internally
(ii) externally Answer
The position vector of point R dividing the line segment joining two points P and Q in the ratio m: n is given by:
i. Internally:
![]()
ii. Externally:
Position vectors of P and Q are given as:
(i) The position vector of point R which divides the line joining two points P and Q internally in the ratio 2:1 is given by,
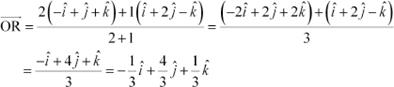
(ii)
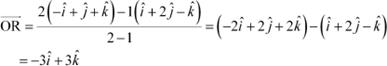 |
The position vector of point R which divides the line joining two points P and Q externally in the ratio 2:1 is given by,
Question 16:
Find the position vector of the mid point of the vector joining the points P (2, 3, 4) and Q (4, 1, – 2).
Answer
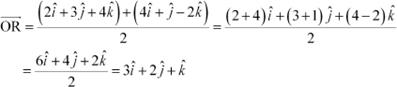 |
The position vector of mid-point R of the vector joining points P (2, 3, 4) and Q (4, 1, – 2) is given by,
Question 17:
![]() Show that the points
A, B and C with position vectors, ,
Show that the points
A, B and C with position vectors, ,
![]() respectively form the vertices of a right
angled triangle. Answer
respectively form the vertices of a right
angled triangle. Answer
Position vectors of points A, B, and C are respectively given as:
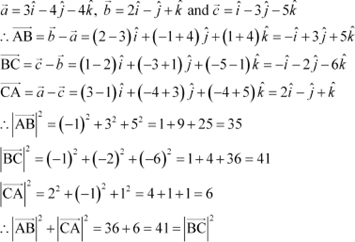 |
Hence, ABC is a right-angled triangle.
Question 18:
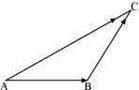 |
In triangle ABC which of the following is not true:
A. ![]()
B. ![]()
C. ![]()
D. ![]()
 |
Answer
On applying the triangle law of addition in the given triangle, we have:
 |
From equations (1) and (3), we have:
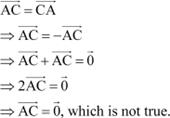 |
Hence, the equation given in alternative C is incorrect. The correct answer is C.
Question 19:
If ![]() are two collinear
vectors, then which of the following are incorrect:
are two collinear
vectors, then which of the following are incorrect:
A. ![]() , for some scalar λ
, for some scalar λ
B. ![]()
C. the respective components of ![]() are proportional
are proportional
D. both the vectors
![]() have same direction, but different magnitudes Answer
have same direction, but different magnitudes Answer
If ![]() are
two collinear vectors, then they are parallel.
Therefore, we have:
are
two collinear vectors, then they are parallel.
Therefore, we have:
![]() (For some scalar λ)
(For some scalar λ)
If λ = ±1, then ![]() .
.
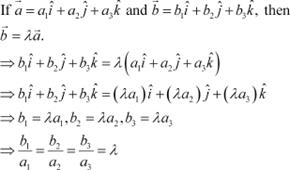 |
Thus, the respective components of ![]() are proportional. However, vectors
are proportional. However, vectors ![]() can have different directions.
can have different directions.
Hence, the statement given in D is incorrect.
The correct answer is D.
Exercise 10.3
Question 1:
![]() Find the angle between
two vectors and
Find the angle between
two vectors and ![]() with magnitudes
with magnitudes ![]() and 2, respectively having
and 2, respectively having ![]() .
.
Answer
It is given that,
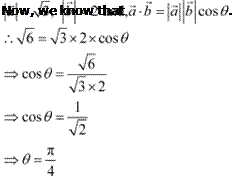 |
![]()
![]() Hence, the angle between
the given vectors and is
Hence, the angle between
the given vectors and is ![]() .
.
Question 2:
Find the angle between
the vectors ![]() Answer
Answer
![]() The given vectors are .
The given vectors are .
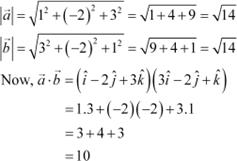
![]() Also, we know that
Also, we know that
.
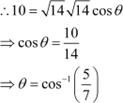 |
Question 3:
Find the projection of the vector
![]() on the vector
on the vector ![]() . Answer
. Answer
Let ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Now, projection of vector ![]() on
on ![]() is given by,
is given by,
Hence, the projection of vector ![]() on
on ![]() is 0.
is 0.
Question 4:
Find the projection of the vector
![]() on the vector
on the vector ![]() . Answer
. Answer
Let ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Now, projection of vector
![]() on
on ![]() is given by,
is given by,
![]()
Question 5:
Show that each of the given three vectors is a unit vector:
Also, show that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. Answer
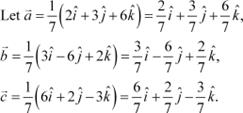
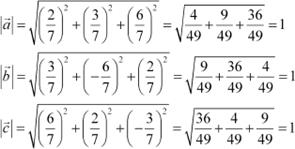 |
Thus, each of the given three vectors is a unit vector.
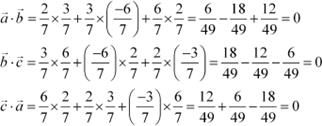 |
Hence, the given three vectors are mutually perpendicular to each other.
Question 6:
Find ![]() and
and ![]() , if
, if ![]() .
.
Answer
 |
Question 7:
Evaluate the product ![]() . Answer
. Answer
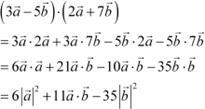 |
Question 8:
Find the magnitude of two vectors
![]() , having the same magnitude and such that
, having the same magnitude and such that
the angle between them is 60° and their scalar product
is ![]() . Answer
. Answer
![]() Let θ be the angle between
the vectors
Let θ be the angle between
the vectors ![]() It is given
that
It is given
that
![]() We know that
We know that
.
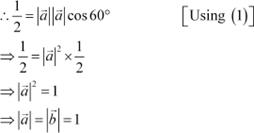 |
Question 9:
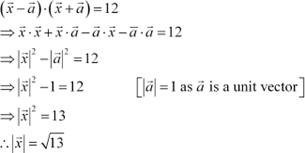 |
Find
Question 10:
![]() If
If ![]() are such that
are such that ![]() is perpendicular to ,
is perpendicular to ,
 |
then find the value of λ. Answer
Hence, the required value of λ is 8.
Question 11:
![]() Show that
Show that ![]() is perpendicular to
is perpendicular to ![]() , for any two nonzero vectors
Answer
, for any two nonzero vectors
Answer
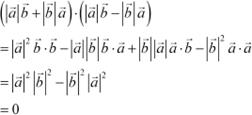 |
Hence, ![]() and
and ![]() are perpendicular to each other.
are perpendicular to each other.
Question 12:
If ![]() , then what can be concluded about the vector
, then what can be concluded about the vector
![]() ?
?
Answer
It is given that ![]() .
.
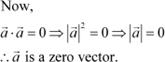 |
Hence, vector ![]() satisfying
satisfying ![]() can be any vector.
can be any vector.
Question 14:
If either vector ![]() , then
, then ![]() . But the converse need not be true. Justify
your answer with an example.
. But the converse need not be true. Justify
your answer with an example.
Answer
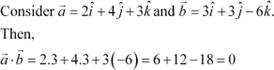 |
We now observe that:
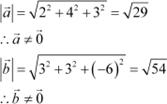 |
Hence, the converse of the given statement need not be true.
Question 15:
If the vertices A, B, C of a triangle ABC are (1, 2, 3), (–1, 0, 0), (0, 1, 2), respectively,
then find ∠ABC. [∠ABC is the angle between
the vectors ![]() and
and ![]() ] Answer
] Answer
The vertices of ∆ABC are given as A (1, 2, 3), B (–1, 0, 0), and C (0, 1, 2). Also, it is given
that ∠ABC is the angle
between the vectors
![]() and
and ![]() .
.
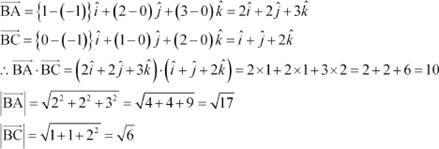
Now, it is known that:
![]() .
.
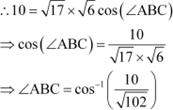 |
Question 16:
Show that the points A (1, 2, 7), B (2, 6, 3) and C (3, 10, –1) are collinear. Answer
The given points are A (1, 2, 7), B (2, 6, 3), and C (3, 10, –1).
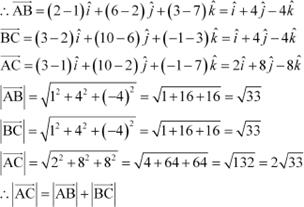 |
Hence, the given points A, B, and C are collinear.
Question 17:
Show that the vectors
![]() form the vertices of a right angled triangle.
form the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Answer
Let vectors
Now, vectors ![]() represent the sides of ∆ABC.
represent the sides of ∆ABC.
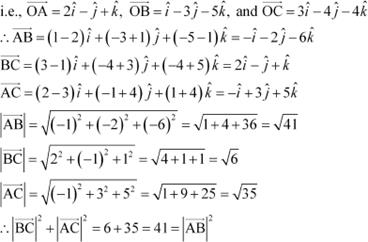 |
Hence, ∆ABC is a right-angled triangle.
Question 18:
![]()
![]() If is a nonzero
vector of magnitude ‘a’ and λ
a nonzero scalar,
then λ
If is a nonzero
vector of magnitude ‘a’ and λ
a nonzero scalar,
then λ ![]() is unit vector if (A) λ
= 1 (B) λ = –1 (C) (D)
is unit vector if (A) λ
= 1 (B) λ = –1 (C) (D) ![]()
Answer
![]() Vector
Vector ![]() is a unit vector
if .
is a unit vector
if .
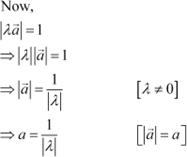
![]() Hence, vector
Hence, vector
![]() is a unit
vector if . The correct
answer is D.
is a unit
vector if . The correct
answer is D.
Exercise 10.4
Question 1:
![]()
![]() Find
Find ![]() , if and . Answer
, if and . Answer
We have,
![]()
![]() and
and
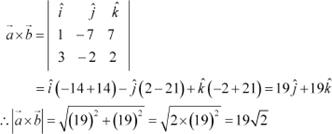 |
Question 2:
Find a unit vector
perpendicular to each of the vector ![]() and
and ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Answer We have,
![]()
![]() and
and
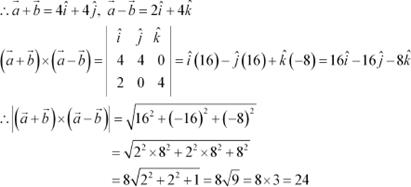 |
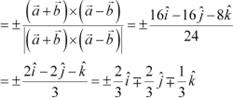 |
Hence, the unit vector perpendicular to each of the vectors
Question 3:
![]()
![]()
![]() If a unit vector makes an angles
If a unit vector makes an angles ![]() with
with ![]() with and an acute angle θ with
, then find θ and
hence, the compounds of
with and an acute angle θ with
, then find θ and
hence, the compounds of ![]() .
.
Answer
Let unit vector ![]() have (a1, a2, a3) components.
have (a1, a2, a3) components.
Since ![]() is a unit vector,
is a unit vector, ![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
![]() Also, it is given that makes angles
Also, it is given that makes angles
![]() with
with ![]() with , and an acute angle θ
with Then, we have:
with , and an acute angle θ
with Then, we have:
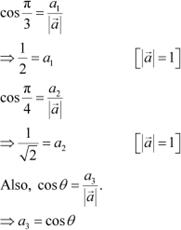 |
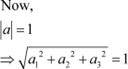
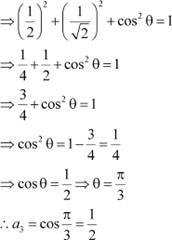 |
![]()
![]() Hence,
Hence, ![]() and the components of are .
and the components of are .
Question 4:
Show that
Answer
 |
Question 5:
![]() Find λ and
µ if .
Find λ and
µ if .
Answer
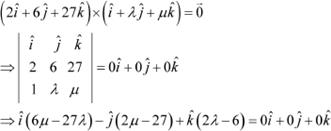 |
On comparing the corresponding components, we have:
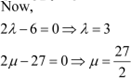 |
Hence, ![]()
Question 6:
Given that
Then,
(i)
Either
(ii) Either ![]() or
or
![]() , or
, or ![]() But,
But,
![]() and
and ![]() cannot be perpendicular and parallel simultaneously.
cannot be perpendicular and parallel simultaneously.
![]()
![]() Hence, or .
Hence, or .
Question 7:
Let the vectors ![]() given as
given as ![]()
![]() . Then
show that
. Then
show that ![]()
Answer We have,
![]()
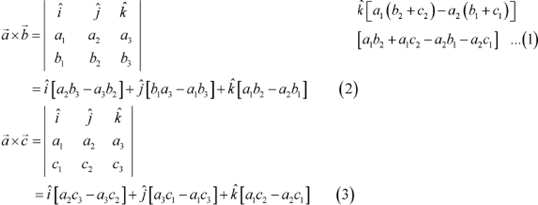 |
On adding (2) and (3), we get:
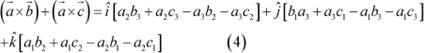 |
Now, from (1) and (4), we have:
Hence, the given result is proved.
Question 8:
If either ![]() or
or ![]() , then
, then ![]() . Is the converse true? Justify your answer with an example.
. Is the converse true? Justify your answer with an example.
Answer
Take any parallel
non-zero vectors so that ![]() .
.
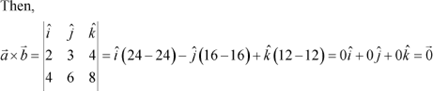 |
It can now be observed that:
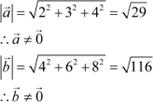 |
Hence, the converse of the given statement need not be true.
Question 9:
Find the area of the triangle with vertices A (1, 1, 2), B (2, 3, 5) and
C (1, 5, 5).
Answer
The vertices of triangle ABC are given as A (1, 1, 2), B (2, 3, 5), and
C (1, 5, 5).
The adjacent sides ![]() and
and ![]() of ∆ABC are given as:
of ∆ABC are given as:
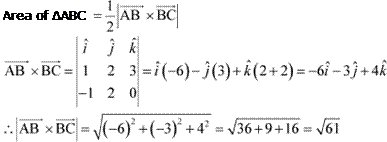
![]() Hence, the area of ∆ABC
Hence, the area of ∆ABC
Question 10:
Find the area of the parallelogram whose adjacent sides are determined by the vector
![]() .
.
Answer
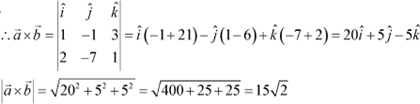 |
Hence, the area of the given
parallelogram is ![]() .
.
Question 11:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Let the vectors and be such that and
Let the vectors and be such that and ![]() , then is a unit vector, if the angle between
, then is a unit vector, if the angle between
![]() and
and ![]() is
is
![]() (A)
(A) ![]() (B)
(B) ![]() (C)
(C) ![]() (D)
(D) ![]() Answer
Answer
It is given that
.
![]()
![]() We know that
We know that ![]() , where is a unit vector perpendicular to both and
, where is a unit vector perpendicular to both and ![]() and θ is
the angle between
and θ is
the angle between
![]() and
and ![]() .
.
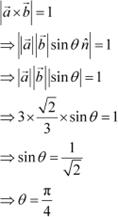 |
![]()
![]()
![]() Hence, is a unit vector
if the angle between and is
Hence, is a unit vector
if the angle between and is ![]() . The correct
answer is B.
. The correct
answer is B.
Question 12:
Area of a rectangle having vertices A, B, C, and D with position vectors
![]() and
and ![]() respectively is
respectively is
(A) ![]() (B) 1
(B) 1
![]() (C) 2 (D) Answer
(C) 2 (D) Answer
The position vectors of vertices A, B, C, and D of rectangle ABCD are given as:
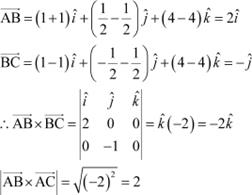 The adjacent sides
The adjacent sides ![]() and
and ![]() of the given rectangle
are given as:
of the given rectangle
are given as:
Now, it is known
that the area of a parallelogram whose adjacent sides
are ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
Hence, the area of the given rectangle is ![]() The correct answer
is C.
The correct answer
is C.
Miscellaneous Solutions
Question 1:
Write down a unit vector in XY-plane, making an angle of 30° with the positive direction of x-axis.
Answer
![]() If is a unit vector in the XY-plane, then
If is a unit vector in the XY-plane, then ![]()
Here, θ is the angle made by the unit vector with the positive direction of the x-axis. Therefore, for θ = 30°:
Hence, the required unit vector is ![]()
Question 2:
Find the scalar components and magnitude of the vector joining the points
![]() .
.
Answer
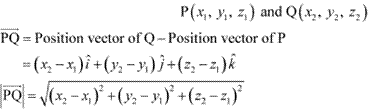 The vector joining the points can be obtained by,
The vector joining the points can be obtained by,
Hence, the scalar components and the magnitude of the vector joining the given points
are respectively ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Question 3:
A girl walks 4 km towards west, then she walks 3 km in a direction 30° east of north and stops. Determine the girl’s displacement from her initial point of departure.
Answer
Let O and B be the initial and final positions of the girl respectively. Then, the girl’s position can be shown as:
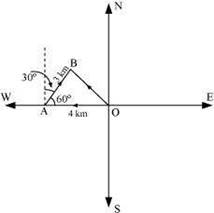
Now, we have:
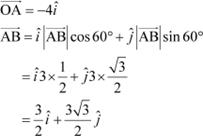 |
By the triangle law of vector addition, we have:
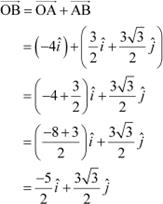 |
Hence, the girl’s displacement from her initial point of departure is
![]() .
.
Question 4:
![]() If , then is it true that
If , then is it true that ![]() ? Justify
your answer. Answer
? Justify
your answer. Answer
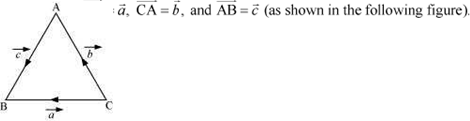 |
Now, by the triangle law of vector addition, we have ![]() .
.
It is clearly known that ![]() represent the sides of ∆ABC.
represent the sides of ∆ABC.
Also, it is known that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
Hence, it is not true that ![]() .
.
Question 5:
Find the value of x for
which ![]() is a unit vector.
Answer
is a unit vector.
Answer
![]()
![]() is a unit vector
if
is a unit vector
if
.
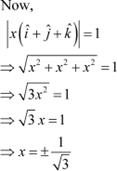
![]() Hence, the required value of x is .
Hence, the required value of x is .
Question 6:
Find a vector of magnitude 5 units, and parallel to the resultant of the vectors
![]() .
.
Answer We have,
![]() Let be the resultant of
Let be the resultant of ![]() .
.
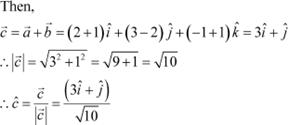 |
Hence, the vector
of magnitude 5 units and parallel to the resultant of vectors ![]() is
is
Question 7:
If ![]() , find a unit vector parallel
to the
, find a unit vector parallel
to the
vector ![]() .
.
Answer We have,
![]()
 |
Hence, the unit vector along ![]() is
is
Question 8:
Show that the points A (1, –2, –8), B (5, 0, –2) and C (11, 3, 7) are collinear, and find the ratio in which B divides AC.
Answer
The given points are A (1, –2, –8), B (5, 0, –2), and C (11, 3, 7).
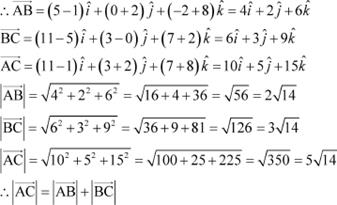 |
Thus, the given points A, B, and C are collinear.
Now, let point B divide AC in the ratio ![]() . Then, we have:
. Then, we have:
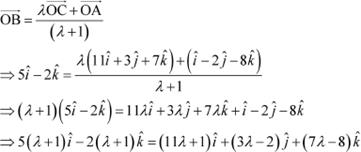 |
On equating the corresponding components, we get:
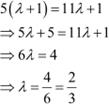 |
Hence, point B divides AC in the ratio ![]()
Question 9:
Find the position vector of a point R which divides the line joining two points P and Q
whose position
vectors are ![]() externally in the ratio 1: 2. Also, show that P is the mid point of the line segment RQ.
externally in the ratio 1: 2. Also, show that P is the mid point of the line segment RQ.
Answer
It is given that ![]() .
.
![]() It is given that point
R divides a line segment joining two points P and Q externally in the ratio
1: 2. Then, on using the section
formula, we get:
It is given that point
R divides a line segment joining two points P and Q externally in the ratio
1: 2. Then, on using the section
formula, we get:
![]() Therefore, the position
vector of point R is
Therefore, the position
vector of point R is ![]() . Position vector of the mid-point of RQ =
. Position vector of the mid-point of RQ =
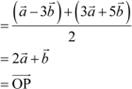
Hence, P is the mid-point of the line segment RQ.
Question 10:
The two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are ![]() and
and ![]() . Find the unit vector
parallel to its diagonal.
Also, find its area.
. Find the unit vector
parallel to its diagonal.
Also, find its area.
Answer
Adjacent sides of a parallelogram are given as: ![]() and
and ![]() Then, the diagonal of a parallelogram is given by
Then, the diagonal of a parallelogram is given by ![]() .
.
![]()
![]() Thus, the unit vector
parallel to the diagonal is
Thus, the unit vector
parallel to the diagonal is
 |
Hence, the area of the parallelogram is ![]() square units.
square units.
Question 11:
Show that the direction cosines of a vector equally inclined to the axes OX, OY and OZ
are ![]() Answer
Answer
Let a vector be equally inclined to axes OX, OY, and OZ at angle α. Then, the direction cosines of the vector are cos α, cos α, and cos α.
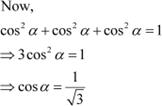
Hence, the direction cosines of the vector which are equally inclined to the axes
![]() are
are
.
Question 12:
Let ![]() and
and ![]() . Find a vector
. Find a vector ![]() which is perpendicular to both
which is perpendicular to both ![]() and
and ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
Answer
Let ![]() .
.
![]() Since
Since ![]() is perpendicular to both and
is perpendicular to both and ![]() , we have:
, we have:
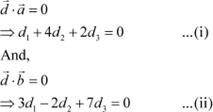 |
Also, it is given that:
On solving (i), (ii), and (iii), we get:
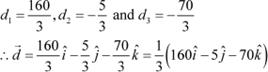 |
Hence, the required vector
is ![]() .
.
Question 13:
![]() The scalar
product of the vector with a unit vector
along the sum of vectors
The scalar
product of the vector with a unit vector
along the sum of vectors
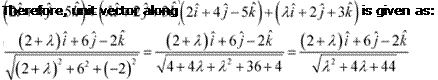 |
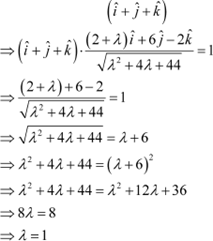 Scalar product
of with this unit vector is 1.
Scalar product
of with this unit vector is 1.
Hence, the value of λ is 1.
Question 14:
If ![]() are mutually
perpendicular vectors of equal magnitudes, show that the vector
are mutually
perpendicular vectors of equal magnitudes, show that the vector
![]() is equally inclined
to
is equally inclined
to ![]() and
and ![]() . Answer
. Answer
Since ![]() are mutually
perpendicular vectors, we have
are mutually
perpendicular vectors, we have
It is given that:
 |
Let vector
![]() Hence, the vector
Hence, the vector ![]() is equally inclined to .
is equally inclined to .
Question 15:
![]() Prove that
Prove that ![]() ,
if and only if are perpendicular, given
,
if and only if are perpendicular, given
![]() .
.
Answer
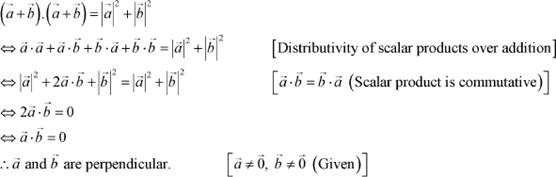 |
Question 16:
If θ is the angle between
two vectors ![]() and
and ![]() , then
, then ![]() only when
only when
(A) ![]() (B)
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]() (D)
(D) ![]()
Answer
Let θ be
the angle between
two vectors ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
![]() Then, without loss of generality,
Then, without loss of generality, ![]() and
and ![]() are non-zero
vectors so that .
are non-zero
vectors so that .
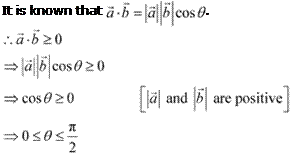
![]() Hence, when
Hence, when
![]() . The correct
answer is B.
. The correct
answer is B.
Question 17:
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be two unit vectors andθ
is the angle between them. Then
be two unit vectors andθ
is the angle between them. Then ![]() is a
unit vector if
is a
unit vector if
(A) ![]() (B)
(B) ![]() (C)
(C) ![]() (D)
(D) ![]() Answer
Answer
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be two unit vectors
andθ be the angle between
them.
be two unit vectors
andθ be the angle between
them.
![]() Then,
Then,
.
![]() Now,
Now, ![]() is a unit vector
if .
is a unit vector
if .
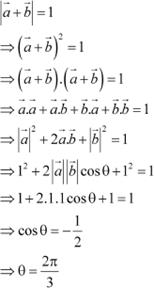
![]() Hence, is a unit vector
if
Hence, is a unit vector
if ![]() . The correct
answer is D.
. The correct
answer is D.
Question 18:
The value of ![]() is
is
(A) 0 (B) –1 (C) 1 (D) 3
Answer
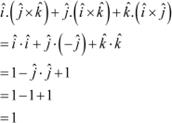 |
The correct answer is C.
Question 19:
![]() If θ
is the angle
between any two vectors
If θ
is the angle
between any two vectors ![]() and
and ![]() , then when θ
isequal to
, then when θ
isequal to
 |
|||
(A) 0 (B) ![]() (C)
(C) ![]() (D) π
Answer
(D) π
Answer
Let θ be
the angle between
two vectors ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
![]() Then, without loss of generality,
Then, without loss of generality, ![]() and
and ![]() are non-zero vectors, so that
are non-zero vectors, so that
.
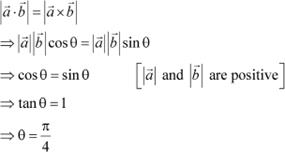 |
![]() Hence,
Hence, ![]() when θ isequal to The correct answer
is B.
when θ isequal to The correct answer
is B.